Newfoundland rod-cone dystrophy, an early-onset retinal dystrophy, is caused by splice-junction mutations in RLBP1
- PMID: 11868161
- PMCID: PMC379124
- DOI: 10.1086/339688
Newfoundland rod-cone dystrophy, an early-onset retinal dystrophy, is caused by splice-junction mutations in RLBP1
Abstract
Some isolated populations exhibit an increased prevalence of rare recessive diseases. The island of Newfoundland is a characteristic geographic isolate, settled by a small number of families primarily during the late 1700s and early 1800s. During our studies of this population, we identified a group of families exhibiting a retinal dystrophy reminiscent of retinitis punctata albescens but with a substantially lower age at onset and more-rapid and distinctive progression, a disorder that we termed "Newfoundland rod-cone dystrophy" (NFRCD). The size of one of these families was sufficient to allow us to perform a genomewide screen to map the NFRCD locus. We detected significant linkage to markers on the long arm of chromosome 15, in a region encompassing RLBP1, the gene encoding the cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein. Previously, mutations in RLBP1 have been associated with other retinal dystrophies, leading us to hypothesize that RLBP1 mutations might also cause NFRCD. To test this hypothesis, we sequenced all coding exons and splice junctions of RLBP1. We detected two sequence alterations, each of which is likely to be pathogenic, since each segregates with the disease and is predicted to interfere with mRNA splicing. In contrast to some previously reported RLBP1 mutations, which yield a protein that may retain some residual activity, each NFRCD mutation is likely to give rise to a null allele. This difference may account for the severe phenotype in these families and exemplifies the molecular continuum that underlies clinically distinct but genetically related entities.
Figures
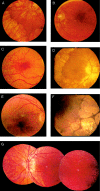
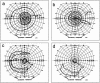
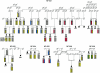
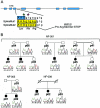
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Delila Server Entry Page, http://www.lecb.ncifcrf.gov/~toms/delilaserver.html
-
- Lupski Lab home page, http://www.imgen.bcm.tmc.edu/molgen/lupski/index.html
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for RLBP1 [MIM 180090], RPA/FA [MIM 136880], and RP [MIM 268000])
References
-
- Beales PL, Katsanis N, Lewis RA, Ansley SJ, Raza J, Woods MO, Green JS, Parfrey PS, Davidson WS, Lupski JR (2001) Genetic and mutational analyses of a large multi-ethnic Bardet-Biedl cohort reveal a minor involvement of BBS6 and delineate the critical intervals of other loci. Am J Hum Genet 68:606–616 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bear JC, Nemec TF, Kennedy JC, Marshall WH, Power AA, Kolonel VM, Burke GB (1988) Inbreeding in outport Newfoundland. Am J Med Genet 29:649–660 - PubMed
-
- Bridges CD, Foster RG, Landers RA, Fong SL (1987) Interstitial retinol-binding protein and cellular retinal-binding protein in the mammalian pineal. Vision Res 27:2049–2060 - PubMed
-
- Burstedt MS, Forsman-Semb K, Golovleva I, Janunger T, Wachtmeister L, Sandgren O (2001) Ocular phenotype of Bothnia dystrophy, an autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa associated with an R234W mutation in the RLBP1 gene. Arch Ophthalmol 119:260–267 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

