IL-4 receptors on human medulloblastoma tumours serve as a sensitive target for a circular permuted IL-4-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein
- PMID: 11870521
- PMCID: PMC2375174
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600034
IL-4 receptors on human medulloblastoma tumours serve as a sensitive target for a circular permuted IL-4-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein
Abstract
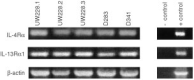
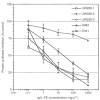
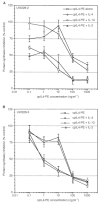
Cytotoxins directed to interleukin-4 receptors have shown to mediate relatively selective cytotoxicity against a variety of human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. In an ongoing Phase I clinical trial, a recombinant protein comprised of circularly permuted IL-4 fused to a mutated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin (the fusion protein termed IL-4(38-37)-PE38KDEL or cpIL4-PE) has shown antitumour activity against malignant glioma. Human medulloblastomas are neuroectodermal tumours that occur in children and have a poor prognosis. The goal of this study was to determine whether human medulloblastoma derived cell lines express interleukin-4 receptor and whether interleukin-4 receptor expression is accompanied by sensitivity to cpIL4-PE. Medulloblastoma cell lines express interleukin-4 receptor at the protein and mRNA levels as determined by binding, indirect immunofluorescence and RT--PCR studies. These cells expressed IL-4Ralpha (also known as IL-4Rbeta) and IL-13Ralpha1 (also known as IL-13Ralpha') chains, however common gamma(c), a component of the interleukin-4 receptor system in immune cells was not detected. Consistent with the expression of IL-4R, cpIL4-PE was found to be highly and specifically cytotoxic to four of five medulloblastoma cell lines. Susceptibility of medulloblastoma cell lines to cpIL4-PE seemed to correlate closely to the functional IL-4 binding sites in general as demonstrated by 125I-IL-4 binding, but did not seem to correlate with mRNA or cell surface immunoreactive receptor protein expression. The sensitivity of medulloblastoma cells to cpIL4-PE could be eliminated by concurrent incubation with IL-4 or IL-13, but not with IL-2. None of these cell lines showed any change in proliferation upon treatment with exogenous IL-4. These studies establish the interleukin-4 receptor as a medulloblastoma-associated target for possible tumour-directed cancer therapy. Further studies are warranted to investigate interleukin-4 receptor expression in primary medulloblastoma tumours and sensitivity to cpIL-4PE in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright 2002 The Cancer Research Campaign
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity in interleukin-13 receptor expression and subunit structure in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: differential sensitivity to chimeric fusion proteins comprised of interleukin-13 and a mutated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Jun;8(6):1948-56. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12060640
-
An improved circularly permuted interleukin 4-toxin is highly cytotoxic to human renal cell carcinoma cells. Introduction of gamma c chain in RCC cells does not improve sensitivity.Cell Immunol. 1996 Jul 10;171(1):80-6. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1996.0176. Cell Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8660841
-
Human breast carcinoma cells express type II IL-4 receptors and are sensitive to antitumor activity of a chimeric IL-4-Pseudomonas exotoxin fusion protein in vitro and in vivo.Mol Med. 2000 Mar;6(3):165-78. Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 10965493 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-4-Pseudomonas exotoxin chimeric fusion protein for malignant glioma therapy.J Neurooncol. 2003 Oct;65(1):15-25. doi: 10.1023/a:1026294416718. J Neurooncol. 2003. PMID: 14649882 Review.
-
Overexpressed cell surface interleukin-4 receptor molecules can be successfully targeted for antitumor cytotoxin therapy.Crit Rev Immunol. 2001;21(1-3):299-310. Crit Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11642612 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor promoting roles of IL-10, TGF-β, IL-4, and IL-35: Its implications in cancer immunotherapy.SAGE Open Med. 2022 Jan 25;10:20503121211069012. doi: 10.1177/20503121211069012. eCollection 2022. SAGE Open Med. 2022. PMID: 35096390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Immunotoxin Therapy of Glioblastoma: Smart Design, Key Findings, and Specific Challenges.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7929286. doi: 10.1155/2017/7929286. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28752098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Photobiomodulation and Akkermansia muciniphila on THP-1 Derived Macrophage Polarization Treated with Gliadin Peptide.J Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Jul 9;15:e21. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2024.21. eCollection 2024. J Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39188931 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments on immunotherapy for brain cancer.Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2012 Jun;17(2):181-202. doi: 10.1517/14728214.2012.679929. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22533851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges in immunotherapy presented by the glioblastoma multiforme microenvironment.Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:732413. doi: 10.1155/2011/732413. Epub 2011 Dec 10. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22190972 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- HoonDSBanezMOkunEMortonDLIrieRF1991Modulation of human melanoma cells by interleukin-4 and in combination with gamma-interferon or alpha-tumor necrosis factor Cancer Res 5120022008 - PubMed
-
- HusainSRBehariNKreitmanRJPastanIPuriRK1998Complete regression of established human glioblastoma tumor xenograft by interleukin-4 toxin therapy Cancer Res 5836493653 - PubMed
-
- HusainSRKreitmanRJPastanIPuriRK1999Interleukin-4 receptor-directed cytotoxin therapy of AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma tumors in xenograft model [see comments] Nat Med 5817822 - PubMed
-
- JoshiBHPlautzGEPuriRK2000Interleukin-13 receptor alpha chain: a novel tumor-associated transmembrane protein in primary explants of human malignant gliomas Cancer Res 6011681172 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

