Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients
- PMID: 11870534
- PMCID: PMC2375266
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600126
Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients
Abstract
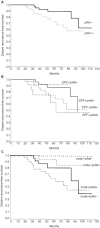
Akt/PKB is a serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell cycle progression, apoptosis and growth factor mediated cell survival in association with tyrosine kinase receptors. The protein is a downstream effector of erbB-2 with implications in breast cancer progression and drug resistance in vitro. We aimed to examine the role of Akt-1 in breast cancer patients, by determining whether the expression (Akt-1) and/or activation (pAkt) were related to prognostic markers and survival. The expression of erbB-2, heregulin beta 1 and Bcl-2 was also assessed by flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry. This study comprised 93 patients, aged <50 who were treated with tamoxifen and/or goserelin. We found that pAkt was associated with lower S-phase fraction (P=0.001) and the presence of heregulin beta 1-expressing stromal cells (P=0.017). Neither Akt-1 nor pAkt was related with other factors. Tumour cells-derived heregulin beta 1 was found mainly in oestrogen receptor negative (P=0.026) and node negative (P=0.005) cases. Survival analysis revealed that pAkt positive patients were more prone to relapse with distant metastasis, independently of S-phase fraction and nodal status (multivariate analysis; P=0.004). The results suggest that activation of Akt may have prognostic relevance in breast cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bad expression predicts outcome in patients treated with tamoxifen.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 Apr;102(2):173-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9323-8. Epub 2006 Sep 27. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 17004114
-
The association between Akt activation and resistance to hormone therapy in metastatic breast cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2006 Mar;42(5):629-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.11.025. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Eur J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16464571
-
Activated Akt signaling pathway in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: correlation with HER2 overexpression.Oncol Rep. 2007 Jul;18(1):139-43. Oncol Rep. 2007. PMID: 17549359
-
Expression of bcl-2 protein predicts efficacy of adjuvant treatments in operable node-positive breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Feb;1(2):189-98. Clin Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 9815973
-
ErbB (HER) receptors can abrogate antiestrogen action in human breast cancer by multiple signaling mechanisms.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jan;9(1 Pt 2):511S-5S. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12538508 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemistry and biology of essential oils of genus boswellia.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:140509. doi: 10.1155/2013/140509. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:605304. doi: 10.1155/2014/605304. PMID: 23533463 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The expression and significance of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its pathway on breast cancer stem/progenitors.Breast Cancer Res. 2013 May 12;15(3):R39. doi: 10.1186/bcr3423. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23663564 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Akt, mTOR, and the estrogen receptor as a signature to predict tamoxifen treatment benefit.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jan;137(2):397-406. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2376-y. Epub 2012 Dec 15. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23242584 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Expression of pAkt is associated with a poor prognosis in Chinese women with invasive ductal breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):4859-4866. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.7965. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552125 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Biophysical Characterization of the Interactions between Calmodulin and the Pleckstrin Homology Domain of Akt.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 6;290(45):27403-27413. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.673939. Epub 2015 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26391397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AguilarZAkitaRWFinnRSRamosBLPegramMDKabbinavarFFPietrasRJPisacanePSliwkowskiMXSlamonDJ1999Biologic effects of heregulin/neu differentiation factor on normal and malignant human breast and ovarian epithelial cells Oncogene 1860506062 - PubMed
-
- AhmadSSinghNGlazerRI1999Role of AKT1 in 17beta-estradiol- and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-dependent proliferation and prevention of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells Biochem Pharmacol 58425430 - PubMed
-
- AhmedNNFrankeTFBellacosaADattaKGonzalez-PortalMETaguchiTTestaJRTsichlisPN1993The proteins encoded by c-akt and v-akt differ in post-translational modification, subcellular localization and oncogenic potential Oncogene 819571963 - PubMed
-
- AndjelkovicMAlessiDRMeierRFernandezALambNJFrechMCronPCohenPLucocqJMHemmingsBA1997Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B J Biol Chem 2723151531524 - PubMed
-
- BacusSSGudkovAVZelnickCRChinDSternRStancovskiIPelesEBen-BaruchNFarbsteinHLupuRWenDSelaMYardenY1993Neu differentiation factor (heregulin) induces expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1: implications for mammary tumors Cancer Res 5352515261 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

