A high vascular count and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor are associated with unfavourable prognosis in operated small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 11870537
- PMCID: PMC2375289
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600130
A high vascular count and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor are associated with unfavourable prognosis in operated small cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
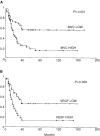
It has been widely demonstrated that neo-angiogenesis and its mediators (i.e. vascular endothelial growth factor), represent useful indicators of poor prognosis in non small cell lung carcinoma. In order to verify whether neovascularization and vascular endothelial growth factor may be considered useful markers of clinical outcome also in the small cell lung cancer subgroup, we retrospectively investigated a series of 75 patients with small cell lung carcinoma treated by surgery between 1980 and 1990. Immunohistochemically-detected microvessels and vascular endothelial growth factor expressing cells were significantly associated with poor prognosis, as well as with nodal status and pathological stage. In fact, patients whose tumours had vascular count and vascular endothelial growth factor expression higher than median value of the entire series (59 vessels per 0.74 mm(2) and 50% of positive cells, respectively), showed a shorter overall and disease-free survival (P=0.001, P=0.001; P=0.008, P=0.03). Moreover, the presence of hilar and/or mediastinal nodal metastasis and advanced stage significantly affected overall and disease-free interval (P=0.00009, P=0.00001; P=0.0001, P=0.00001). At multivariate analysis, only vascular endothelial growth factor expression retained its influence on overall survival (P=0.001), suggesting that angiogenic phenomenon may have an important role in the clinical behaviour of this lung cancer subgroup.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer correlates with neoangiogenesis and a poor prognosis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2001 Jan-Feb;8(1):72-9. doi: 10.1007/s10434-001-0072-y. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11206229
-
Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC): the angiogenic phenomenon.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002 Jun;21(6):1105-10. doi: 10.1016/s1010-7940(02)00112-4. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002. PMID: 12048093
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: prognostic significance in squamous cell carcinoma.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998 May;115(5):1007-14. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70398-8. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998. PMID: 9605068
-
Prognostic value of vascularity and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in non-small cell lung cancer.J Clin Pathol. 2001 Feb;54(2):116-20. doi: 10.1136/jcp.54.2.116. J Clin Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11215279 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer.Oncologist. 2000;5 Suppl 1:37-44. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.5-suppl_1-37. Oncologist. 2000. PMID: 10804090 Review.
Cited by
-
Theranostic tumor homing nanocarriers for the treatment of lung cancer.Nanomedicine. 2014 Jul;10(5):1053-63. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24355163 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of thalidomide-based therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2014;18(1):39-47. doi: 10.5114/wo.2014.40782. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2014. PMID: 24876820 Free PMC article.
-
Apatinib with etoposide capsules as a third- or further-line therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: an open-label, multicenter, single-arm phase II trial.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;10(2):889-899. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1235. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33718030 Free PMC article.
-
New molecularly targeted therapies for lung cancer.J Clin Invest. 2007 Oct;117(10):2740-50. doi: 10.1172/JCI31809. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17909619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009 Apr 15;6(2):206-17. doi: 10.1513/pats.200807-066LC. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009. PMID: 19349490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-JawdehGMFaixJDNiloffJTognazziKManseauEDvorakHFBrownLF1996Strong expression of vascular endothelial permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in ovarian borderline and malignant neoplasms Lab Invest 611051115 - PubMed
-
- American Joint Committee on Cancer1992Manual for a staging of cancer4th edn,pp115122
-
- ApolinarioRMvan der ValkPde JongJSDevilleWvan Ark-OtteJDingemansAMvan MourikJCPostmusPEPinedoHMGiacconeG1997Prognostic value of p53, bcl-2, and bax oncoprotein and neovascularization in patients with radically-resected non-small cell lung cancer J Clin Oncol 1524562466 - PubMed
-
- BicknellRHarrisAL1991Novel growth regulatory factors and tumor angiogenesis Eur J Cancer 27781785 - PubMed
-
- BouckN1996p53 and angiogenesis Biochem Biophys Acta 12876366 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical