Two different lantibiotic-like peptides originate from the ericin gene cluster of Bacillus subtilis A1/3
- PMID: 11872722
- PMCID: PMC134901
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.6.1703-1711.2002
Two different lantibiotic-like peptides originate from the ericin gene cluster of Bacillus subtilis A1/3
Abstract
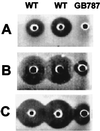
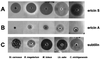
A lantibiotic gene cluster was identified in Bacillus subtilis A1/3 showing a high degree of homology to the subtilin gene cluster and occupying the same genetic locus as the spa genes in B. subtilis ATCC 6633. The gene cluster exhibits diversity with respect to duplication of two subtilin-like genes which are separated by a sequence similar to a portion of a lanC gene. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) analyses of B. subtilis A1/3 culture extracts confirmed the presence of two lantibiotic-like peptides, ericin S (3,442 Da) and ericin A (2,986 Da). Disruption of the lanB-homologous gene eriB resulted in loss of production of both peptides, demonstrating that they are processed in an eriB-dependent manner. Although precursors of ericins S and A show only 75% of identity, the matured lantibiotic-like peptides reveal highly similar physical properties; separation was only achieved after multistep, reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Based on Edman and peptidase degradation in combination with MALDI-TOF MS, for ericin S a subtilin-like, lanthionine-bridging pattern is supposed. For ericin A two C-terminal rings are different from the lanthionine pattern of subtilin. Due to only four amino acid exchanges, ericin S and subtilin revealed similar antibiotic activities as well as similar properties in response to heat and protease treatment. For ericin A only minor antibiotic activity was found.
Figures




References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1995. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Banerjee, S., and J. N. Hansen. 1988. Structure and expression of a gene encoding the precursor of subtilin, a small protein antibiotic. J. Biol. Chem. 263:9508-9514. - PubMed
-
- Borchert, S., S. S. Patil, and M. A. Marahiel. 1992. Identification of putative multifunctional peptide synthetase genes using highly conserved oligonucleotide sequences derived from known synthetases. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 92:175-180. - PubMed
-
- Breukink, E., and B. de Kruijff. 1999. The lantibiotic nisin, a special case or not? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1462:223-234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

