5-HT1B-receptors and vascular reactivity in human isolated blood vessels: assessment of the potential craniovascular selectivity of sumatriptan
- PMID: 11874390
- PMCID: PMC1874302
- DOI: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01536.x
5-HT1B-receptors and vascular reactivity in human isolated blood vessels: assessment of the potential craniovascular selectivity of sumatriptan
Abstract
Aims: 5-HT1B-receptor mediated vasoconstriction of cranial arteries is a potential mechanism by which 5-HT1B/1D-receptor agonists such as sumatriptan produce their antimigraine effects. 5-HT1B-receptors exist in other blood vessels which may give rise to unwanted vascular effects. Therefore we examined the distribution of 5-HT1B-receptor immunoreactivity (i.r.) in human blood vessels (including target and nontarget vessels) and confirmed the functionality of this receptor protein, by comparing the vasoconstrictor effects of sumatriptan and 5-HT (the endogenous ligand) in isolated vessels.
Methods: Blood vessels (middle meningeal, pial, temporal and uterine arteries and saphenous veins) were obtained from surgical patients (with consent). Sections of the vessels were prepared for routine immunohistochemical studies using specific 5-HT1B- and 5-HT1D-receptor antibodies. For functional studies, ring segments of the vessels were mounted in organ baths for isometric tension recording.
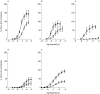
Results: 5-HT1B-receptor i.r. was detected on the smooth muscle layer in middle meningeal, pial and uterine arteries and in saphenous vein and sumatriptan produced contractions in these vessels with potency values (mean pEC50) of 7.00, 7.08, 6.44 and 6.61, respectively, the magnitude of contraction was greatest in the cranial arteries with Emax values of 100.7, 60.3, 23.0 and 35.9%, respectively (expressed as a percentage of the reference agonist 45 mm KCl). 5-HT1B-receptor i.r. was not detected in temporal artery and sumatriptan had no effect in this artery. 5-HT1D-receptor i.r. was not detected in any of the vessels studied.
Conclusions: Sumatriptan can evoke vasoconstriction in antimigraine target vessels and also in nontarget vessels through an action at 5-HT1B-rcceptors. Sumatriptan acts preferentially to cause contraction in human cranial arteries compared with the other blood vessels we examined and this effect is likely to be shared by other drugs of this class.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the vasoconstrictor effects of rizatriptan and sumatriptan in human isolated cranial arteries: immunohistological demonstration of the involvement of 5-HT1B-receptors.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Dec;46(6):577-82. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00821.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9862247 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the vasoconstrictor effects of the selective 5-HT1D-receptor agonist L-775,606 with the mixed 5-HT1B/1D-receptor agonist sumatriptan and 5-HT in human isolated coronary artery.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;49(2):126-31. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00129.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10671906 Free PMC article.
-
Vasoconstriction in human isolated middle meningeal arteries: determining the contribution of 5-HT1B- and 5-HT1F-receptor activation.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1999 Jan;47(1):75-82. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00851.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10073743 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT receptors mediating external carotid vasoconstriction in vagosympathectomized dogs.Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999 Dec;20(12):1057-67. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999. PMID: 11216445 Review.
-
[Anti-migraine drug sumatriptan succinate, a 5-HT1B/1D-receptor agonist].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Jun;117(6):387-93. doi: 10.1254/fpj.117.387. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11436516 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Drug Safety in Episodic Migraine Management in Adults Part 1: Acute Treatments.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022 Jul;26(7):481-492. doi: 10.1007/s11916-022-01057-3. Epub 2022 May 10. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022. PMID: 35536501 Review.
-
The complex actions of sumatriptan on rat dural afferents.Cephalalgia. 2012 Jul;32(10):738-49. doi: 10.1177/0333102412451356. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Cephalalgia. 2012. PMID: 22711897 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin and blood pressure regulation.Pharmacol Rev. 2012 Apr;64(2):359-88. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004697. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Pharmacol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22407614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basilar artery occlusion in migraine-like headache: a possible triggering effect of sumatriptan.Neurol Sci. 2012 Feb;33(1):125-8. doi: 10.1007/s10072-011-0651-z. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Neurol Sci. 2012. PMID: 21681368
-
Serotonergic Modulation of Neurovascular Transmission: A Focus on Prejunctional 5-HT Receptors/Mechanisms.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 29;11(7):1864. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071864. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, et al. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) Pharmacol Rev. 1996;46:157–203. - PubMed
-
- Bax WA, van Heuven-Nolsen D, Bos E, Somoons ML, Saxena PR. 5-Hydroxytryptamine-induced contractions of the human isolated saphenous vein: involvement of 5-HT2 and 5-HT1D-like receptors, and a comparison with grafted veins. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. 1992;345:500–508. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

