Long term anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: effect on radiological course and prognostic value of markers of cartilage turnover and endothelial activation
- PMID: 11874832
- PMCID: PMC1754066
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.61.4.311
Long term anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: effect on radiological course and prognostic value of markers of cartilage turnover and endothelial activation
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effect of prolonged neutralisation of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) on the radiological course in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To assess whether the radiological course can be predicted by clinical variables or biological markers of cartilage and synovium turnover and of endothelial activation.
Patients and methods: Forty seven patients with active RA enrolled at our centre in monotherapy trials with adalimumab (D2E7), a fully human anti-TNFalpha monoclonal antibody, were studied for two years. Radiographs of hands and feet obtained at baseline and after one and two years were scored in chronological order by a single, blinded observer using the modified Sharp method. Radiological course was classified as stable or progressive using the smallest detectable difference as cut off point. The relation between radiological course and serum markers of cartilage and synovium turnover (metalloproteinases (MMP-1 and MMP-3), cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), human cartilage glycoprotein-39 (HC gp-39)), endothelial activation (soluble E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1)), and integrated measures of disease activity were assessed using univariate and multivariate analysis.
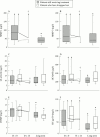
Results: Radiological evaluation was performed in 36 patients with paired sets of radiographs at baseline and two years. After two years a total of 15/36 (42%) presented no radiological progression. More patients with stable radiological course were still receiving anti-TNFalpha treatment after two years (13/15 (87%) v 11/21 (52%); p=0.03) and had lower baseline COMP and sICAM-1 levels (p=0.01 and 0.04, respectively) than those in the group with progressive disease. In a logistic regression model the combination of sustained TNF neutralisation and baseline COMP and sICAM-1 levels was predictive for radiological outcome (p=0.03). C reactive protein and disease activity score area under the curve were significantly correlated with changes in radiological scores after two years (r=0.40 and 0.37, p<0.05). Long term TNFalpha neutralisation decreased the levels of COMP, sICAM, MMPs, and HC gp-39, but not sE-selectin.
Conclusion: The results suggest that long term monotherapy with anti-TNFalpha has a positive effect on radiological outcome and modulates cartilage and synovium turnover as measured by biological markers. Baseline serum sICAM-1 levels and COMP levels may be helpful to identify patients with progressive or non-progressive radiological outcome.
Figures


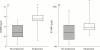
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

