Which patients stop working because of rheumatoid arthritis? Results of five years' follow up in 732 patients from the Early RA Study (ERAS)
- PMID: 11874837
- PMCID: PMC1754067
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.61.4.335
Which patients stop working because of rheumatoid arthritis? Results of five years' follow up in 732 patients from the Early RA Study (ERAS)
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the occurrence and prognostic factors for the ability to maintain paid work in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Setting: Inception cohort of patients with RA recruited from rheumatology departments in nine NHS Hospital Trusts in England.
Patients: All consecutive patients with RA of less than two years' duration, before any second line (disease modifying) drug treatment, and followed up for five years.
Methods: Clinical, laboratory, and radiological assessments, and all treatments were recorded prospectively using a standardised format at presentation and yearly.
Outcome measures: Changes in, and loss of paid work by five years' follow up.
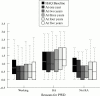
Results: 732 patients completed the five year follow up. 353/721 (49%) were gainfully employed at the onset of RA, 211 (60%) were still working at five years, 104 (29%) stopped because of the disease, and 31 (9%) retired for reasons other than RA. Work disability at five years was more likely in manual workers (odds ratio (OR) 2.3, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.4 to 3.8) and worse baseline Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ>1.5, OR 2.26, 95% CI 1.38 to 3.7). In combination with other baseline variables (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, sex, age of onset, and radiological erosions), employment outcome was predicted in 78% using multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: Nearly half of the patients with RA were in paid employment at onset, work disability was an adverse outcome for a third of these patients by five years, and manual work and high baseline HAQ were important predictors for this. These details are likely to be useful to clinicians, health professionals, and patients in order to plan medical, orthopaedic, and remedial treatments in early RA. Future disease modifying treatments could be compared with this cohort of patients who were treated with conventional second line drugs.
Figures
Comment in
-
Which patients stop working because of RA?Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Sep;61(9):859; author reply 859. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.9.859. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002. PMID: 12176824 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
How does functional disability in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affect patients and their lives? Results of 5 years of follow-up in 732 patients from the Early RA Study (ERAS).Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000 Jun;39(6):603-11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.6.603. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000. PMID: 10888704
-
The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on employment status in the early years of disease: a UK community-based study.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000 Dec;39(12):1403-9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.12.1403. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000. PMID: 11136885
-
Work disability rates in RA. Results from an inception cohort with 24 years follow-up.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 Feb;51(2):385-92. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker401. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22237045
-
Databases of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis in the USA.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003 Sep-Oct;21(5 Suppl 31):S146-53. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14969067 Review.
-
Assessing prognosis and prediction of treatment response in early rheumatoid arthritis: systematic reviews.Health Technol Assess. 2018 Nov;22(66):1-294. doi: 10.3310/hta22660. Health Technol Assess. 2018. PMID: 30501821 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influence of rheumatoid arthritis-related morning stiffness on productivity at work: results from a survey in 11 European countries.Rheumatol Int. 2015 Nov;35(11):1791-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3275-4. Epub 2015 May 26. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 26007151
-
A structured literature review of the burden of illness and unmet needs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a current perspective.Rheumatol Int. 2016 May;36(5):685-95. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3415-x. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26746843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long term safety of etanercept in elderly subjects with rheumatic diseases.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Mar;65(3):379-84. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.035287. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16150792 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective cohort study of presenteeism and increased risk of unemployment among Japanese workers during the COVID-19 pandemic.J Occup Health. 2024 Jan 4;66(1):uiad015. doi: 10.1093/joccuh/uiad015. J Occup Health. 2024. PMID: 38344801 Free PMC article.
-
Cost effectiveness of tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors as first-line agents in rheumatoid arthritis.Pharmacoeconomics. 2006;24(12):1221-32. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200624120-00006. Pharmacoeconomics. 2006. PMID: 17129076
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical