Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections
- PMID: 11874871
- PMCID: PMC119950
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.9.2.324-328.2002
Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections
Abstract
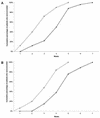
African tick-bite fever, caused by Rickettsia africae, is the most common tick-borne rickettsiosis in sub-Saharan Africa. Mediterranean spotted fever due to Rickettsia conorii also occurs in the region but is more prevalent in Mediterranean countries. Using microimmunofluorescence, we compared the development of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM titers in 48 patients with African tick-bite fever and 48 patients with Mediterranean spotted fever. Doxycycline treatment within 7 days from the onset of disease significantly prevented the development of antibodies to R. africae. In patients with African tick-bite fever, the median times to seroconversion with IgG and IgM were 28 and 25 days, respectively, after the onset of symptoms. These were significantly longer by a median of 6 days for IgG and 9 days for IgM than the times for seroconversion in patients with Mediterranean spotted fever (P < 10(-2)). We recommend that sera collected 4 weeks after the onset of signs of patients with suspected African tick-bite fever should be used for the definitive serological diagnosis of R. africae infections.
Figures

References
-
- Beati, L., N. Teysseire, and D. Raoult. 1992. Kinetics of specific antibodies in Mediterranean spotted fever determined by Western blotting and microimmunofluorescence. Acta Virol. 36:62-66. - PubMed
-
- Fournier, P. E., V. Roux, E. Caumes, M. Donzel, and D. Raoult. 1998. Outbreak of Rickettsia africae infections in participants of an adventure race from South Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 27:316-323. - PubMed
-
- Hechemy, K. E., D. Raoult, J. Fox, Y. Han, L. B. Elliott, and J. Rawlings. 1989. Cross-reaction of immune sera from patients with rickettsial diseases. J. Med. Microbiol. 29:199-202. - PubMed
-
- Kelly, P. J., L. Beati, P. R. Mason, L. A. Matthewman, V. Roux, and D. Raoult. 1996. Rickettsia africae sp nov, the etiological agent of African tick bite fever. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46:611-614. - PubMed
-
- McDade, J. E. 1991. Evidence supporting the hypothesis that rickettsial virulence factors determine the severity of spotted fever and typhus group infections. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Science 590:20-26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

