Sensitive microplate assay for detection of bactericidal antibodies to Vibrio cholerae O139
- PMID: 11874883
- PMCID: PMC119965
- DOI: 10.1128/cdli.9.2.383-387.2002
Sensitive microplate assay for detection of bactericidal antibodies to Vibrio cholerae O139
Abstract
A microplate assay for the detection of bactericidal antibodies to Vibrio cholerae O139 is described. The assay is sensitive, highly reproducible, specific, and convenient to perform. It has been used to demonstrate the induction of serum bactericidal antibodies in Vietnamese recipients of an oral, inactivated, bivalent O1/O139 vaccine, as well as in Bangladeshi patients with O139 disease. In both study groups there was a significant inverse correlation between the preexposure level of antibodies in serum and the magnitude of the subsequent bactericidal response. Although infection generated stronger responses than vaccination, the proportion of responders was similar among individuals with low background titers.
Figures
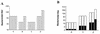
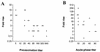
References
-
- Attridge, S. R. 1991. Oral immunisation with Salmonella typhi Ty21a-based clones expressing Vibrio cholerae O antigen: serum bactericidal antibody responses in man in relation to pre-immunisation antibody levels. Vaccine 9:877-882. - PubMed
-
- Cholera Working Group. 1993. Large epidemic of cholera-like disease in Bangladesh caused by Vibrio cholerae O139 synonym Bengal. Lancet 342:387-390. - PubMed
-
- Coster, T. S., K. P. Killeen, M. K. Waldor, D. T. Beattie, D. R. Spriggs, J. R. Kenner, A. Trofa, J. C. Sadoff, J. J. Mekalanos, and D. N. Taylor. 1995. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of live attenuated Vibrio cholerae O139 vaccine prototype. Lancet 345:949-952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

