Myelin protein P0-specific IgM producing monoclonal B cell lines were established from polyneuropathy patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
- PMID: 11876747
- PMCID: PMC1906329
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01739.x
Myelin protein P0-specific IgM producing monoclonal B cell lines were established from polyneuropathy patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
Abstract
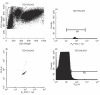
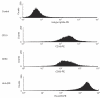
Monoclonal expansion of B cells and plasma cells, producing antibodies against 'self' molecules, can be found not only in different autoimmune diseases, such as peripheral neuropathy (PN), but also in malignancies, such as Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia and B-type of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL), as well as in precancerous conditions including monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). About 50% of patients with PN-MGUS have serum antibodies against peripheral nerve myelin, but the specific role of these antibodies remains uncertain. The aims of the study were to establish, and characterize, myelin-specific B cell clones from peripheral blood of patients with PN-MGUS, by selection of cells bearing specific membrane Ig-receptors for myelin protein P0, using beads coated with P0. P0-coated magnetic beads were used for selection of cells, which subsequently were transformed by Epstein--Barr virus. The specificity of secreted antibodies was tested by ELISA. Two of the clones producing anti-P0 antibodies were selected and expanded. The magnetic selection procedure was repeated and new clones established. The cells were CD5+ positive, although the expression declined in vitro over time. The anti-P0 antibodies were of IgM-lambda type. The antibodies belonged to the VH3 gene family with presence of somatic mutations. The IgM reacted with P0 and myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG), and showed no evidence for polyreactivity, in contrast to other IgM CD5+ clones included in the study as controls. The expanded clones expressed CD80 and HLA-DR, which is compatible with properties of antigen-presenting cells. The immunomagnetic selection technique was successfully used for isolation of antimyelin protein P0-specific clones. The cell lines may provide useful tools in studies of monoclonal gammopathies, leukaemia, and autoimmune diseases, including aspects of antigen-presentation by these cells followed by T cell activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Myelin protein zero is naturally processed in the B cells of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance of immunoglobulin M isotype: aberrant triggering of a patient's T cells.Haematologica. 2010 Apr;95(4):627-36. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.015123. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20015874 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal IgM rheumatoid factor secreted by CD5-negative B cells during mixed cryoglobulinemia. Evidence for somatic mutations and intraclonal diversity of the expressed VH region gene.J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):413-21. J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7527818
-
CD5 expression on B cells may be an activation marker for secretion of anti-myelin antibodies in patients with polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy.Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Aug;101(2):346-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb08362.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7544252 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal IgM autoantibody reactivity in M-IgM peripheral neuropathy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2000 Aug;19(1):7-18. doi: 10.1385/CRIAI:19:1:7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11064822 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Neuropathy associated with dysglobulinemia and monoclonal gammopathy].Nihon Rinsho. 1994 Nov;52(11):2976-83. Nihon Rinsho. 1994. PMID: 7996697 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Myelin protein zero is naturally processed in the B cells of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance of immunoglobulin M isotype: aberrant triggering of a patient's T cells.Haematologica. 2010 Apr;95(4):627-36. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.015123. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20015874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vrethem M. Polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy. 1994. A clinical, neurophysiological andimmunological study. Linköping University Medical Dissertation, no. 409. - PubMed
-
- Gorson KC. Clinical features, evaluation, and treatment of patients with polyneuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) J Clin Apheresis. 1999;14:149–53. 10.1002/(sici)1098-1101(1999)14:3<149::aid-jca8>3.0.co;2-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shannessy DJ, Ilyas AA, Dalakas MC, et al. Specificity of human IgM monoclonal antibodies from patients with peripheral neuropathy. J Neuroimmunol. 1986;11:131–6. - PubMed
-
- Bollensen E, Steck AJ, Schachner M. Reactivity with the peripheral myelin glycoprotein P0 in serum from patients with monoclonal IgM gammopathy and polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1988;38:1266–70. - PubMed
-
- Quarles RH. Human monoclonal antibodies associated with neuropathy. Meth Enzymol. 1989;179:291–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

