Molecular diversity of phospholipase D in angiosperms
- PMID: 11876823
- PMCID: PMC77410
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-3-2
Molecular diversity of phospholipase D in angiosperms
Abstract
Background: The phospholipase D (PLD) family has been identified in plants by recent molecular studies, fostered by the emerging importance of plant PLDs in stress physiology and signal transduction. However, the presence of multiple isoforms limits the power of conventional biochemical and pharmacological approaches, and calls for a wider application of genetic methodology.
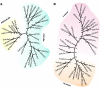
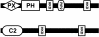
Results: Taking advantage of sequence data available in public databases, we attempted to provide a prerequisite for such an approach. We made a complete inventory of the Arabidopsis thaliana PLD family, which was found to comprise 12 distinct genes. The current nomenclature of Arabidopsis PLDs was refined and expanded to include five newly described genes. To assess the degree of plant PLD diversity beyond Arabidopsis we explored data from rice (including the genome draft by Monsanto) as well as cDNA and EST sequences from several other plants. Our analysis revealed two major PLD subfamilies in plants. The first, designated C2-PLD, is characterised by presence of the C2 domain and comprises previously known plant PLDs as well as new isoforms with possibly unusual features catalytically inactive or independent on Ca2+. The second subfamily (denoted PXPH-PLD) is novel in plants but is related to animal and fungal enzymes possessing the PX and PH domains.
Conclusions: The evolutionary dynamics, and inter-specific diversity, of plant PLDs inferred from our phylogenetic analysis, call for more plant species to be employed in PLD research. This will enable us to obtain generally valid conclusions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide and molecular evolution analyses of the phospholipase D gene family in Poplar and Grape.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Jun 18;10:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-117. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20565843 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the phospholipase D family in Oryza sativa and functional characterization of PLD beta 1 in seed germination.Cell Res. 2007 Oct;17(10):881-94. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.77. Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17876344
-
A transmembrane phospholipase D in Phytophthora; a novel PLD subfamily.Gene. 2005 May 9;350(2):173-82. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.02.012. Epub 2005 Apr 9. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15826868
-
Phospholipase D in hormonal and stress signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002 Oct;5(5):408-14. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00283-2. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002. PMID: 12183179 Review.
-
Plant phospholipase D: novel structure, regulatory mechanism, and multifaceted functions with biotechnological application.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022 Feb;42(1):106-124. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1924113. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34167393 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of a phospholipase D gene, OsPLDbeta1, activates defense responses and increases disease resistance in rice.Plant Physiol. 2009 May;150(1):308-19. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.131979. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19286937 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of the Phospholipase D Gene Family in Solanum tuberosum.Biology (Basel). 2021 Aug 2;10(8):741. doi: 10.3390/biology10080741. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439973 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase d activation correlates with microtubule reorganization in living plant cells.Plant Cell. 2003 Nov;15(11):2666-79. doi: 10.1105/tpc.014977. Epub 2003 Sep 24. Plant Cell. 2003. PMID: 14508002 Free PMC article.
-
Allelopathic enhancement and differential gene expression in rice under low nitrogen treatment.J Chem Ecol. 2008 May;34(5):688-95. doi: 10.1007/s10886-008-9455-x. Epub 2008 Apr 8. J Chem Ecol. 2008. PMID: 18392895
-
Signalling Pinpointed to the Tip: The Complex Regulatory Network That Allows Pollen Tube Growth.Plants (Basel). 2020 Aug 26;9(9):1098. doi: 10.3390/plants9091098. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32859043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanahan DJ, Chaikoff IL. A new phospholipide-splitting enzyme specific for the ester linkage between the nitrogenous base and the phosphoric acid grouping. J Biol Chem. 1947;169:699–705. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Xu L, Zheng L. Cloning and expression of phosphatidylcholine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D from Ricinus communis L. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20312–20317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

