Effect of SEA0400, a novel inhibitor of sodium-calcium exchanger, on myocardial ionic currents
- PMID: 11877314
- PMCID: PMC1573238
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704574
Effect of SEA0400, a novel inhibitor of sodium-calcium exchanger, on myocardial ionic currents
Abstract
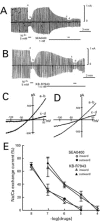
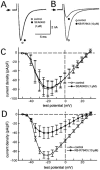
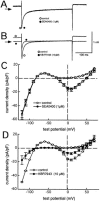
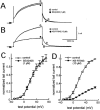
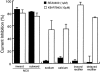
The effects of 2-[4-[(2,5-difluorophenyl) methoxy]phenoxy]-5-ethoxyaniline (SEA0400), a newly synthesized Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) inhibitor, on the NCX current and other membrane currents were examined in isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes and compared with those of 2-[2-[4-(4-nitrobenzyloxy) phenyl]ethyl]isothiourea (KB-R7943). SEA0400 concentration-dependently inhibited the NCX current with a 10 fold higher potency than that of KB-R7943; 1 microM SEA0400 and 10 microM KB-R7943 inhibited the NCX current by more than 80%. KB-R7943, at 10 microM, inhibited the sodium current, L-type calcium current, delayed rectifier potassium current and inwardly rectifying potassium current by more than 50%, but SEA0400 (1 microM) had no significant effect on these currents. These results indicate that SEA0400 is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of NCX, and would be a powerful tool for further studies on the role of NCX in the heart and the therapeutic potential of its inhibition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of SEA0400 and KB-R7943 on Na+/Ca2+ exchange current and L-type Ca2+ current in canine ventricular cardiomyocytes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;372(1):63-70. doi: 10.1007/s00210-005-1079-x. Epub 2005 Aug 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16086157
-
SEA0400, a novel and selective inhibitor of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger, attenuates reperfusion injury in the in vitro and in vivo cerebral ischemic models.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Jul;298(1):249-56. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11408549
-
Protective effects of SEA0400, a novel and selective inhibitor of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injuries.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Jan 1;458(1-2):155-62. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(02)02732-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12498920
-
Functional proteins involved in regulation of intracellular Ca(2+) for drug development: pharmacology of SEA0400, a specific inhibitor of the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger.J Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Mar;97(3):339-43. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj04007x2. Epub 2005 Mar 12. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15764845 Review.
-
[Functional analysis of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger using novel drugs and genetically engineered mice].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2002 Nov;120(1):91P-93P. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 12491791 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Effects of SEA0400 and KB-R7943 on Na+/Ca2+ exchange current and L-type Ca2+ current in canine ventricular cardiomyocytes.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;372(1):63-70. doi: 10.1007/s00210-005-1079-x. Epub 2005 Aug 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16086157
-
Endothelial nitric oxide attenuates Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-mediated vasoconstriction in rat aorta.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;154(5):982-90. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.178. Epub 2008 May 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18469841 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of sodium-calcium exchanger by SEA-0400 decreases early and delayed after depolarization in canine heart.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Dec;143(7):827-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706026. Epub 2004 Oct 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15504749 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of artemether toxicity on single cardiomyocytes and protective effect of nanoencapsulation.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;177(19):4448-4463. doi: 10.1111/bph.15186. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32608017 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-dependent recovery of ionised magnesium concentration following magnesium load in rat heart myocytes.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Feb;451(5):657-67. doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-1501-8. Epub 2005 Aug 16. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16133259
References
-
- BERS D.M. Calcium fluxes involved in control of cardiac myocyte contraction. Circ. Res. 2000;87:275–281. - PubMed
-
- FABIATO A., FABIATO F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J. Physiol. (Paris) 1979;75:463–505. - PubMed
-
- KATO Y., MASUMIYA H., AGATA N., TANAKA H., SHIGENOBU K. Developmental changes in action potential and membrane currents in fetal, neonatal and adult guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1996;28:1515–1522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

