Proteinase-activated receptor-1 agonists attenuate nociception in response to noxious stimuli
- PMID: 11877315
- PMCID: PMC1573232
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704568
Proteinase-activated receptor-1 agonists attenuate nociception in response to noxious stimuli
Abstract
Proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) is activated by thrombin and can be selectively activated by synthetic peptides (PAR-1-activating peptide: PAR-1-AP) corresponding to the receptor's tethered ligand. PAR-1 being expressed by afferent neurons, we investigated the effects of PAR-1 agonists on nociceptive responses to mechanical and thermal noxious stimuli. Intraplantar injection of selective PAR-1-AP increased nociceptive threshold and withdrawal latency, leading to mechanical and thermal analgesia, while control peptide had no effect. Intraplantar injection of thrombin also showed analgesic properties in response to mechanical, but not to thermal stimulus. Co-injection of PAR-1-AP with carrageenan significantly reduced carrageenan-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia, while thrombin reduced carrageenan-induced mechanical but not thermal hyperalgesia. The fact that thrombin is not a selective agonist for PAR-1 may explain the different effects of thrombin and PAR-1-AP. These results identified analgesic properties for selective PAR-1 agonists that can modulate nociceptive response to noxious stimuli in normal and inflammatory conditions.
Figures
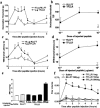

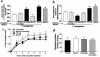
References
-
- BAR-SHAVIT R., KAHN A., MUDD M., WILNER G., MANN K., FENTON J. Localization of a chemotactic domain in human thrombin. Biochemistry. 1984;23:397–400. - PubMed
-
- BAR-SHAVIT R., KAHN A., WILNER G., FENTON J. Monocyte chemotaxis: stimulation by specific exosite region in thrombin. Science. 1983;220:728–731. - PubMed
-
- DE GARAVILLA L., VERGNOLLE N., YOUNG S.H., ENNES H., STEINHOFF M., OSSOVSKAYA V.S., D'ANDREA M.R., MAYER E.A., WALLACE J.L., HOLLENBERG M.D., ANDRADE-GORDON P., BUNNETT N.W. Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 1 induce plasma extravasation by a neurogenic mechanism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001;133:975–987. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

