Platelet-activating factor drives eotaxin production in an allergic pleurisy in mice
- PMID: 11877329
- PMCID: PMC1573234
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704570
Platelet-activating factor drives eotaxin production in an allergic pleurisy in mice
Abstract
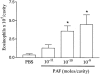
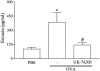
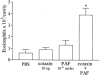
1. The activation of eosinophils via G-protein-coupled seven transmembrane receptors play a necessary role in the recruitment of these cells into tissue. The present study investigates a role for PAF in driving eotaxin production and eosinophil recruitment in an allergic pleurisy model in mice. 2. The intrapleural injection of increasing doses of PAF (10(-11) to 10(-9) moles per cavity) induced a dose- and PAF receptor-dependent recruitment of eosinophils 48 h after stimulation. 3. Intrapleural injection of PAF induced the rapid (within 1 h) release of eotaxin into the pleural cavity of mice and an anti-eotaxin antibody effectively inhibited PAF-induced recruitment of eosinophils. 4. Eosinophil recruitment in the allergic pleurisy was markedly inhibited by the PAF receptor antagonist UK-74,505 (modipafant, 1 mg kg(-1)). Moreover, recruitment of eosinophils in sensitized and challenged PAF receptor-deficient animals was lower than that observed in wild-type animals. 5. Blockade of PAF receptors with UK-74,505 suppressed by 85% the release of eotaxin in the allergic pleurisy. 6. Finally, the injection of a sub-threshold dose of PAF and eotaxin cooperated to induce eosinophil recruitment in vivo. 7. In conclusion, the production of PAF in an allergic reaction could function in multiple ways to facilitate the recruitment of eosinophils -- by facilitating eotaxin release and by cooperating with eotaxin to induce greater recruitment of eosinophils.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stem cell factor-induced leukotriene B4 production cooperates with eotaxin to mediate the recruitment of eosinophils during allergic pleurisy in mice.J Immunol. 2001 Jul 1;167(1):524-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.524. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11418691
-
The role of CCL22 (MDC) for the recruitment of eosinophils during allergic pleurisy in mice.J Leukoc Biol. 2003 Mar;73(3):356-62. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0502243. J Leukoc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12629149
-
Modulation of eotaxin formation and eosinophil migration by selective inhibitors of phosphodiesterase type 4 isoenzyme.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Sep;134(2):283-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704233. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11564646 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of platelet-activating factor to allergen-induced eosinophil infiltration and bronchial hyperresponsiveness.Lipids. 1991 Dec;26(12):1280-2. doi: 10.1007/BF02536548. Lipids. 1991. PMID: 1819716 Review.
-
[Analysis of chemical mediators involved in acute inflammatory reaction with the rat pleurisy model].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1997 Aug;110(2):59-68. doi: 10.1254/fpj.110.59. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1997. PMID: 9306414 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Intragranular vesiculotubular compartments are involved in piecemeal degranulation by activated human eosinophils.Traffic. 2005 Oct;6(10):866-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00322.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 16138901 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-activating factor and protease-activated receptor 2 cooperate to promote neutrophil recruitment and lung inflammation through nuclear factor-kappa B transactivation.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 7;13(1):21637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48365-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38062077 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-activating factor receptor deficiency delays elimination of adult worms but reduces fecundity in Strongyloides venezuelensis-infected mice.Infect Immun. 2004 Feb;72(2):1135-42. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.1135-1142.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14742561 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PAF receptors during intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury. A comparative study between PAF receptor-deficient mice and PAF receptor antagonist treatment.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;139(4):733-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705296. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12812996 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effects of tachykinin receptor antagonists on eosinophil recruitment in an allergic pleurisy model in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;140(5):847-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705515. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14585802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALABASTER V.A., KEIR R.F., PARRY M.J., DE SOUZA R.N. UK-74505, a novel and selective PAF antagonist, exhibits potent and long lasting activity in vivo. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;34:221–227. - PubMed
-
- ALVES A.C., PIRES A.L., CRUZ H.N., SERRA M.F., DIAZ B.L., CORDEIRO R.S., LAGENTE V., MARTINS M.A. Selective inhibition of phosphodiesterase type IV suppresses the chemotactic responsiveness of rat eosinophils in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996;312:89–96. - PubMed
-
- AU B.T., TEIXEIRA M.M., COLLINS P.D., WILLIAMS T.J. Blockade of PAF receptors controls IL-8 production by regulating the activation of neutrophil CD11/CD18. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001;425:65–71. - PubMed
-
- BARTEMES K.R., MCKINNEY S., GLEICH G.J., KITA H. Endogenous platelet-activating factor is critically involved in effector functions of eosinophils stimulated with IL-5 or IgG. J. Immunol. 1999;162:2982–2989. - PubMed
-
- BORGES C.M., SILVEIRA M.R., BEKER M.A., FREIRE-MAIA L., TEIXEIRA M.M. Scorpion venom-induced neutrophilia is inhibited by a PAF receptor antagonist in the rat. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000;67:515–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

