Permeability of porcine blood brain barrier to somatostatin analogues
- PMID: 11877340
- PMCID: PMC1573221
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704557
Permeability of porcine blood brain barrier to somatostatin analogues
Abstract
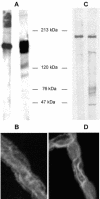
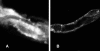
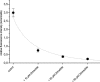
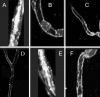
1. Transport of a fluorescent somatostatin analogue (NBD-octreotide) across freshly isolated functionally intact capillaries from porcine brain was visualized by confocal microscopy and quantitated by image analysis. 2. Luminal accumulation of NBD-octreotide showed all characteristics of specific and energy-dependent transport. Steady-state luminal fluorescence averaged 2 - 3 times cellular fluorescence and was reduced to cellular levels when metabolism was inhibited by NaCN. 3. The accumulation of NBD-octreotide in capillary lumens was inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner by unlabelled octreotide, by verapamil, PSC-833 and cyclosporin A, potent inhibitors of p-glycoprotein, and by leucotriene C(4), a strong modulator of Mrp2. Conversely, unlabelled octreotide reduced luminal accumulation of fluorescent BODIPY-verapamil on p-glycoprotein and of fluorescein-methotrexate, on Mrp2. None of the inhibitors used significantly reduced cellular accumulation of the fluorescent substrates. 4. Together, the data are consistent with octreotide being transported across the luminal membrane of porcine brain capillaries by both P-gp and Mrp2, providing further evidence that both transporters contribute substantially to the active barrier function of this endothelium.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ivermectin excretion by isolated functionally intact brain endothelial capillaries.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Feb;132(3):722-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703762. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11159725 Free PMC article.
-
P-glycoprotein- and mrp2-mediated octreotide transport in renal proximal tubule.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jan;129(2):251-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703003. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10694230 Free PMC article.
-
Xenobiotic transport across isolated brain microvessels studied by confocal microscopy.Mol Pharmacol. 2000 Dec;58(6):1357-67. doi: 10.1124/mol.58.6.1357. Mol Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11093774
-
Functional expression and localization of P-glycoprotein at the blood brain barrier.Microsc Res Tech. 2002 Jun 1;57(5):365-80. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10090. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 12112443 Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier biology and methodology.J Neurovirol. 1999 Dec;5(6):556-69. doi: 10.3109/13550289909021285. J Neurovirol. 1999. PMID: 10602397 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of transendothelial permeability and expression of ATP-binding cassette transporters in cultured brain capillary endothelial cells by astrocytic factors and cell-culture conditions.Exp Brain Res. 2003 Dec;153(3):356-65. doi: 10.1007/s00221-003-1620-4. Epub 2003 Sep 12. Exp Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 14610630
-
Vascular cognitive impairment: Modeling a critical neurologic disease in vitro and in vivo.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1862(5):975-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26704178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatostatin: Linking Cognition and Alzheimer Disease to Therapeutic Targeting.Pharmacol Rev. 2024 Oct 16;76(6):1291-1325. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.124.001117. Pharmacol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39013601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Therapeutic Peptide for Cachexia Suggests a Platform Approach for Drug-like Peptides.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Apr 14;5(5):344-361. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00270. eCollection 2022 May 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35592439 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for abnormal glucose uptake or metabolism in thalamus during acute hyperglycaemia in type 1 diabetes--a 1H MRS study.Metab Brain Dis. 2010 Jun;25(2):227-34. doi: 10.1007/s11011-010-9199-5. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Metab Brain Dis. 2010. PMID: 20424902
References
-
- ABBRUSCATO T.J., THOMAS S.A., HRUBY V.J., DAVIS T.P. Blood-brain barrier permeability and bioavailability of a highly potent and μ-selective opioid receptor antagonist, CTAP: comparison with morphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997;250:402–409. - PubMed
-
- BANKS W.A., KASTIN A.J. Peptides and the blood-brain barrier: lipophilicity as a predictor of permeability. Brain Res. Bull. 1985;15:287–292. - PubMed
-
- BANKS W.A., KASTINA A.J., SAM H.M., CAO V.T., KING B., MANESS L.M., SCHALLY A.V. Saturable efflux of the peptides RC-160 and Tyr-MIF-1 by different parts of the blood brain barrier. Brain Res. Bull. 1994;35:179–182. - PubMed
-
- BEGLEY D.J. The interaction of some centrally active drugs with the blood-brain barrier and circumventricular organs. Prog. Brain Res. 1992;91:163–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

