Allergenic sensitization prevents upregulation of haemopoiesis by cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors in mice
- PMID: 11877341
- PMCID: PMC1573244
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704580
Allergenic sensitization prevents upregulation of haemopoiesis by cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors in mice
Abstract
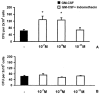
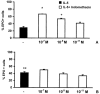
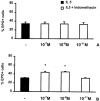
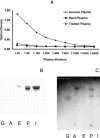
1. We evaluated whether immunization affects bone-marrow responses to indomethacin, because allergenic sensitization and challenge upregulate responses to haemopoietic cytokines (including IL-5-driven eosinopoiesis) in murine bone-marrow, while indomethacin upregulates haemopoiesis and protects bone-marrow from radiation damage. 2. Progenitor (semi-solid) and/or precursor (liquid) cultures were established from bone-marrow of: (a) normal mice; (b) ovalbumin-sensitized mice, with or without intranasal challenge. Cultures were established with GM-CSF (2 ng ml(-1)) or IL-5 (1 ng ml(-1)), respectively, alone or associated with indomethacin (10(-7) - 10(-11) M) or aspirin (10(-7) - 10(-8) M). Total myeloid colony numbers and numbers of eosinophil-peroxidase-positive cells were determined at day 7. 3. In naïve BALB/c mice, indomethacin (10(-7) - 10(-9) M) increased GM-CSF-stimulated myeloid colony formation (P=0.003 and P=0.009, respectively). In contrast, it had no effect on bone-marrow of ovalbumin-sensitized and challenged mice. Indomethacin (10(-7) - 10(-9) M) also increased eosinophil precursor responses to IL-5 in bone-marrow of naïve (P<0.001 and P=0.002 respectively), but not sensitized-challenged mice. Aspirin (10(-7) M) had similar effects, equally abolished by sensitization. Enhancement of haemopoiesis by indomethacin required adherent cells from naïve bone-marrow. Nonadherent cells responded to IL-5 but not to indomethacin. Indomethacin was effective on bone-marrow from sham-sensitized, ovalbumin-challenged, but not from sensitized, saline-challenged mice. Plasma transfer from immune mice abolished eosinophil precursor responses to indomethacin in bone-marrow of naïve recipients. This was not prevented by previous removal of antibody from immune plasma. 4. COX inhibitors enhance haemopoiesis in naïve but not allergic mice. Responsiveness to indomethacin can be abolished either by active sensitization or by immune plasma transfer. Specific antibody is not involved.
Figures

References
-
- AIZAWA S., HIRAMOTO M., ARAKI S., NEGISHI S., KIMURA Y., HOSHI H., KOJIMA S., WAKASUGI K. Stimulatory effects of neopterin on haemopoiesis in vitro are mediated by activation of stromal cell function. Hematol. Oncol. 1998;16:57–67. - PubMed
-
- AMADORI A., WIRLEITNER B., DIEZ-RUIZ A., VERONESI A., CHIECO-BIANCHI L., FUCHS D. Neopterin production in SCID mice injected with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Immunobiology. 2001;203:642–649. - PubMed
-
- BAIER-BITTERLICH G., FUCHS D., WACHTER H. Chronic Immune stimulation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in HIV infection. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997;53:755–763. - PubMed
-
- BAGBY G.C.Haemopoiesis The Molecular Basis of Blood Diseases 1994Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders; 71–106.In Stamatoyannopoulos2nd edn. ed. Nienhuis, G.A.W., Majerus, P.W., Varmus, H. pp
-
- CAMPANILE F., GIAMPIETRI A., GROHMANN U., BINAGLIA L., FIORETTI M.C., PUCCETTI P. Accelerated hematopoietic recovery and protective effect of the COX inhibitor indomethacin in bacterial infection of neutropenic mice. Cell. Immunol. 147:341–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

