Proteasome inhibition reduces superantigen-mediated T cell activation and the severity of psoriasis in a SCID-hu model
- PMID: 11877475
- PMCID: PMC150886
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12736
Proteasome inhibition reduces superantigen-mediated T cell activation and the severity of psoriasis in a SCID-hu model
Abstract
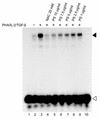
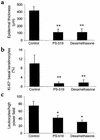
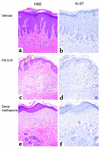
There is increasing evidence that bacterial superantigens contribute to inflammation and T cell responses in psoriasis. Psoriatic inflammation entails a complex series of inductive and effector processes that require the regulated expression of various proinflammatory genes, many of which require NF-kappa B for maximal trans-activation. PS-519 is a potent and selective proteasome inhibitor based upon the naturally occurring compound lactacystin, which inhibits NF-kappa B activation by blocking the degradation of its inhibitory protein I kappa B. We report that proteasome inhibition by PS-519 reduces superantigen-mediated T cell-activation in vitro and in vivo. Proliferation was inhibited along with the expression of very early (CD69), early (CD25), and late T cell (HLA-DR) activation molecules. Moreover, expression of E-selectin ligands relevant to dermal T cell homing was reduced, as was E-selectin binding in vitro. Finally, PS-519 proved to be therapeutically effective in a SCID-hu xenogeneic psoriasis transplantation model. We conclude that inhibition of the proteasome, e.g., by PS-519, is a promising means to treat T cell-mediated disorders such as psoriasis.
Figures

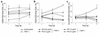


References
-
- Acha-Orbea, H. 1995. Superantigens and tolerance. In T cell receptors. J.I. Bell, M.J. Owen, and E. Simpson, editors. Oxford University Press. Oxford, United Kingdom. 224–265.
-
- Zollner TM, Nuber V, Duijvestijn AM, Boehncke WH, Kaufmann R. Superantigens but not mitogens are capable of inducing upregulation of E-selectin ligands on human T lymphocytes. Exp Dermatol. 1997;6:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Zollner TM, et al. The superantigen exfoliative toxin induces cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen expression in peripheral human T lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 1996;49:111–116. - PubMed
-
- Paliard X, et al. Evidence for the effects of a superantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Science. 1991;253:325–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

