Therapeutic effects of coenzyme Q10 and remacemide in transgenic mouse models of Huntington's disease
- PMID: 11880489
- PMCID: PMC6758854
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-05-01592.2002
Therapeutic effects of coenzyme Q10 and remacemide in transgenic mouse models of Huntington's disease
Abstract
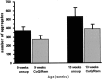
There is substantial evidence that bioenergetic defects and excitotoxicity may play a role in the pathogenesis of Huntington's disease (HD). Potential therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases in which there is reduced energy metabolism and NMDA-mediated excitotoxicity are the administration of the mitochondrial cofactor coenzyme Q10 and the NMDA antagonist remacemide. We found that oral administration of either coenzyme Q10 or remacemide significantly extended survival and delayed the development of motor deficits, weight loss, cerebral atrophy, and neuronal intranuclear inclusions in the R6/2 transgenic mouse model of HD. The combined treatment, using coenzyme Q10 and remacemide together, was more efficacious than either compound alone, resulting in an approximately 32 and 17% increase in survival in the R6/2 and N171-82Q mice, respectively. Magnetic resonance imaging showed that combined treatment significantly attenuated ventricular enlargement in vivo. These studies further implicate defective energy metabolism and excitotoxicity in the R6/2 and N171-82Q transgenic mouse models of HD and are of interest in comparison with the outcome of a recent clinical trial examining coenzyme Q10 and remacemide in HD patients.
Figures




References
-
- Abe K, Fujimura H, Nishikawa Y, Yorifuki S, Mezaki T, Hirono N, Nishitani N, Kameyama M. Marked reduction in CSF lactate and pyruvate levels after CoQ therapy in a patient with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS). Acta Neurol Scand. 1991;83:356–359. - PubMed
-
- Bannan PE, Graham DI, Lees KR, McCulloch J. Neuroprotective effect of remacemide hydrochloride in focal cerebral ischemia in the cat. Brain Res. 1994;664:271–275. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF. Energetics in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:294–300. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Kowall NW, Ellison DW, Mazurek MF, Swartz KJ, Martin JB. Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington's disease by quinolinic acid. Nature. 1986;321:4181–4192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
