Caspase-3-dependent proteolytic cleavage of protein kinase Cdelta is essential for oxidative stress-mediated dopaminergic cell death after exposure to methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl
- PMID: 11880503
- PMCID: PMC6758879
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-05-01738.2002
Caspase-3-dependent proteolytic cleavage of protein kinase Cdelta is essential for oxidative stress-mediated dopaminergic cell death after exposure to methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl
Abstract
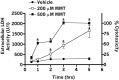
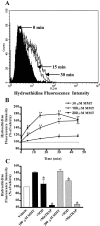
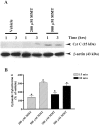
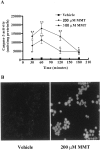
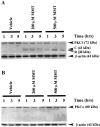
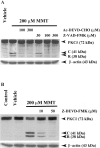
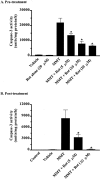
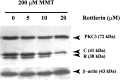
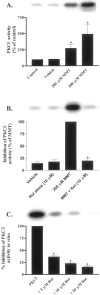
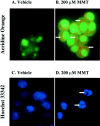
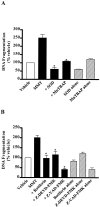
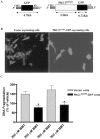
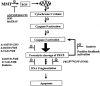
In the present study, we characterized oxidative stress-dependent cellular events in dopaminergic cells after exposure to an organic form of manganese compound, methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (MMT). In pheochromocytoma cells, MMT exposure resulted in rapid increase in generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) within 5--15 min, followed by release of mitochondrial cytochrome C into cytoplasm and subsequent activation of cysteine proteases, caspase-9 (twofold to threefold) and caspase-3 (15- to 25-fold), but not caspase-8, in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, we also found that MMT exposure induces a time- and dose-dependent proteolytic cleavage of native protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta, 72-74 kDa) to yield 41 kDa catalytically active and 38 kDa regulatory fragments. Pretreatment with caspase inhibitors (Z-DEVD-FMK or Z-VAD-FMK) blocked MMT-induced proteolytic cleavage of PKCdelta, indicating that cleavage is mediated by caspase-3. Furthermore, inhibition of PKCdelta activity with a specific inhibitor, rottlerin, significantly inhibited caspase-3 activation in a dose-dependent manner along with a reduction in PKCdelta cleavage products, indicating a possible positive feedback activation of caspase-3 activity by PKCdelta. The presence of such a positive feedback loop was also confirmed by delivering the catalytically active PKCdelta fragment. Attenuation of ROS generation, caspase-3 activation, and PKCdelta activity before MMT treatment almost completely suppressed DNA fragmentation. Additionally, overexpression of catalytically inactive PKCdelta(K376R) (dominant-negative mutant) prevented MMT-induced apoptosis in immortalized mesencephalic dopaminergic cells. For the first time, these data demonstrate that caspase-3-dependent proteolytic activation of PKCdelta plays a key role in oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in dopaminergic cells after exposure to an environmental neurotoxic agent.
Figures
References
-
- Ajiro K. Histone H2B phosphorylation in mammalian apoptotic cells An association with DNA fragmentation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:439–443. - PubMed
-
- Autissier N, Dumas P, Brosseau J, Loireau A. Effects of methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (MMT) of rat liver mitochondria. I. Effects, in vitro, on the oxidative phosphorylation. Toxicology. 1977;7:115–122. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau A. Manganese and extrapyramidal disorders (a critical review and tribute to Dr. George C Cotzias). Neurotoxicology. 1984;5:13–35. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Woolard MD, Johnson CL. Involvement of protein kinase C-delta in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001;8:899–908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
