An algorithm and program for finding sequence specific oligonucleotide probes for species identification
- PMID: 11882251
- PMCID: PMC100321
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-3-9
An algorithm and program for finding sequence specific oligonucleotide probes for species identification
Abstract
Background: The identification of species or species groups with specific oligo-nucleotides as molecular signatures is becoming increasingly popular for bacterial samples. However, it shows also great promise for other small organisms that are taxonomically difficult to tract.
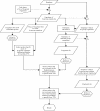
Results: We have devised here an algorithm that aims to find the optimal probes for any given set of sequences. The program requires only a crude alignment of these sequences as input and is optimized for performance to deal also with very large datasets. The algorithm is designed such that the position of mismatches in the probes influences the selection and makes provision of single nucleotide outloops. Program implementations are available for Linux and Windows.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oligonucleotide probes based on 16S rRNA sequences for the identification of four Azospirillum species.Can J Microbiol. 1995 Dec;41(12):1081-7. doi: 10.1139/m95-151. Can J Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8542552
-
Oligonucleotide probes for Bordetella bronchiseptica based on 16S ribosomal RNA sequences.Vet Microbiol. 1994 Dec;42(4):297-305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(94)90061-2. Vet Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 9133055
-
Oligo Design: a computer program for development of probes for oligonucleotide microarrays.Biotechniques. 2003 Dec;35(6):1216-21. doi: 10.2144/03356bc02. Biotechniques. 2003. PMID: 14682056
-
In situ detection of freshwater fungi in an alpine stream by new taxon-specific fluorescence in situ hybridization probes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Oct;74(20):6427-36. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00815-08. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18776035 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of characteristic oligonucleotides in the bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA sequence dataset.Bioinformatics. 2002 Feb;18(2):244-50. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.244. Bioinformatics. 2002. PMID: 11847072
Cited by
-
Reverse taxonomy: an approach towards determining the diversity of meiobenthic organisms based on ribosomal RNA signature sequences.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Oct 29;360(1462):1917-24. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1723. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16214749 Free PMC article.
-
An algorithm for the determination and quantification of components of nucleic acid mixtures based on single sequencing reactions.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Nov 29;6:281. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-281. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16316462 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of custom microarray applications: the oligonucleotide design challenge.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(6):1726-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp053. Epub 2009 Feb 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19208645 Free PMC article.
-
PrimerStation: a highly specific multiplex genomic PCR primer design server for the human genome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W665-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl297. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845094 Free PMC article.
-
Universal fingerprinting chip server.Bioinformation. 2012;8(12):586-8. doi: 10.6026/97320630008586. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Bioinformation. 2012. PMID: 22829736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- E DeLong, G Wickham, N Pace. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989;243:1360–1363. - PubMed
-
- The ARB project. http://www.arb-home.de/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

