Digital analysis of cDNA abundance; expression profiling by means of restriction fragment fingerprinting
- PMID: 11882253
- PMCID: PMC99051
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-3-7
Digital analysis of cDNA abundance; expression profiling by means of restriction fragment fingerprinting
Abstract
Background: Gene expression profiling among different tissues is of paramount interest in various areas of biomedical research. We have developed a novel method (DADA, Digital Analysis of cDNA Abundance), that calculates the relative abundance of genes in cDNA libraries.
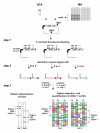
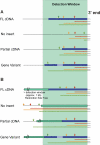
Results: DADA is based upon multiple restriction fragment length analysis of pools of clones from cDNA libraries and the identification of gene-specific restriction fingerprints in the resulting complex fragment mixtures. A specific cDNA cloning vector had to be constructed that governed missing or incomplete cDNA inserts which would generate misleading fingerprints in standard cloning vectors. Double stranded cDNA was synthesized using an anchored oligo dT primer, uni-directionally inserted into the DADA vector and cDNA libraries were constructed in E. coli. The cDNA fingerprints were generated in a PCR-free procedure that allows for parallel plasmid preparation, labeling, restriction digest and fragment separation of pools of 96 colonies each. This multiplexing significantly enhanced the throughput in comparison to sequence-based methods (e.g. EST approach). The data of the fragment mixtures were integrated into a relational database system and queried with fingerprints experimentally produced by analyzing single colonies. Due to limited predictability of the position of DNA fragments on the polyacrylamid gels of a given size, fingerprints derived solely from cDNA sequences were not accurate enough to be used for the analysis. We applied DADA to the analysis of gene expression profiles in a model for impaired wound healing (treatment of mice with dexamethasone).
Conclusions: The method proved to be capable of identifying pharmacologically relevant target genes that had not been identified by other standard methods routinely used to find differentially expressed genes. Due to the above mentioned limited predictability of the fingerprints, the method was yet tested only with a limited number of experimentally determined fingerprints and was able to detect differences in gene expression of transcripts representing 0.05% of the total mRNA population (e.g. medium abundant gene transcripts).
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Analysis, identification and correction of some errors of model refseqs appeared in NCBI Human Gene Database by in silico cloning and experimental verification of novel human genes].Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004 May;31(5):431-43. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15478601 Chinese.
-
A new set of ESTs and cDNA clones from full-length and normalized libraries for gene discovery and functional characterization in citrus.BMC Genomics. 2009 Sep 11;10:428. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-428. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19747386 Free PMC article.
-
Non-stoichiometric reduced complexity probes for cDNA arrays.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Sep 1;26(17):3883-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.17.3883. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9705494 Free PMC article.
-
Peanut gene expression profiling in developing seeds at different reproduction stages during Aspergillus parasiticus infection.BMC Dev Biol. 2008 Feb 4;8:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-8-12. BMC Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18248674 Free PMC article.
-
Hybridization fingerprinting of high-density cDNA-library arrays with cDNA pools derived from whole tissues.Mamm Genome. 1992;3(11):609-19. doi: 10.1007/BF00352477. Mamm Genome. 1992. PMID: 1450511
References
-
- Deleersnijder W, Hong G, Cortvrindt R, Poirier C, Tylzanowski P, Pittois K, Van Marck E, Merregaert J. Isolation of markers for chondro-osteogenic differentiation using cDNA library subtraction. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene belonging to a novel multigene family of integral membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:19475–82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.32.19475. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Diatchenko L, Lau YF, Campbell AP, Chenchik A, Moqadam F, Huang B, Lukyanov S, Lukyanov K, Gurskaya N, Sverdlov ED, Siebert PD. Suppression subtractive hybridization: a method for generating differentially regulated or tissue-specific cDNA probes and libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:6025–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.12.6025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gurskaya NG, Diatchenko L, Chenchik A, Siebert PD, Khaspekov GL, Lukyanov KA, Vagner LL, Ermolaeva OD, Lukyanov SA, Sverdlov ED. Equalizing cDNA subtraction based on selective suppression of polymerase chain reaction: cloning of Jurkat cell transcripts induced by phytohemaglutinin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Anal Biochem. 1996;240:90–7. doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0334. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

