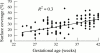Deposition of whole blood platelets on extracellular matrix under flow conditions in preterm infants
- PMID: 11882557
- PMCID: PMC1721386
- DOI: 10.1136/fn.86.2.f127
Deposition of whole blood platelets on extracellular matrix under flow conditions in preterm infants
Abstract
Background: A previous study showed greater adhesion by platelets of healthy full term infants to subendothelial extracellular matrix (ECM) under flow conditions compared with healthy adult platelets.
Aim: To investigate the adhesion and aggregation of platelets from preterm infants on ECM under defined shear conditions.
Methods: In vitro platelet function was investigated in 106 preterm infants, 74 full term infants, and 26 healthy adults. Blood samples were obtained from all infants within 24 hours of birth, and weekly until discharge from preterm infants only. Citrated whole blood was placed in ECM precoated tissue culture plates and subjected to shear stress (1300 s-1) for two minutes using a rotating Teflon cone. Platelet adhesion (surface coverage) and aggregation (average size) to ECM were assayed using an image analyser. Assays for von Willebrand factor (vWF) antigen, ristocetin cofactor, and vWF collagen-binding activity were performed on samples from an additional 70 preterm infants, 23 healthy full term infants, and 24 healthy adults. Preterm infants with hyaline membrane disease (HMD) were analysed separately in both cohorts.
Results: Platelets from preterm infants displayed significantly less platelet adhesion than those from full term infants but similar aggregation and levels of vWF antigen, ristocetin cofactor, and collagen binding activity. Mean surface coverage was 22.0 (8.4)% for preterm infants with HMD, 28.7 (8.0)% for healthy preterm infants, and 35.7 (7.9)% for full term infants. Surface coverage in the preterm infants correlated with gestational age during the first 24 hours only, and did not reach full term levels during 10 weeks of follow up.
Conclusion: Platelet adhesion to ECM is significantly poorer in preterm than in full term infants, and poorer in preterm infants with HMD than in healthy preterm infants. Intrinsic platelet properties rather than the concentration or activity of vWF may be responsible for this difference.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole blood platelet deposition on extracellular matrix under flow conditions in preterm neonatal sepsis.Eur J Pediatr. 2002 May;161(5):270-4. doi: 10.1007/s00431-002-0938-4. Epub 2002 Mar 16. Eur J Pediatr. 2002. PMID: 12012223
-
Increased neonatal platelet deposition on subendothelium under flow conditions: the role of plasma von Willebrand factor.Pediatr Res. 1999 Feb;45(2):270-5. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199902000-00019. Pediatr Res. 1999. PMID: 10022601
-
Dynamic platelet function on von Willebrand factor is different in preterm neonates and full-term neonates: changes in neonatal platelet function.J Thromb Haemost. 2016 Oct;14(10):2027-2035. doi: 10.1111/jth.13414. Epub 2016 Aug 20. J Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 27416003
-
Platelet-vessel wall interactions in thrombosis and restenosis role of von Willebrand factor.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1997;59(3):161-83. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1997. PMID: 9490916 Review.
-
Platelets and shear stress.Blood. 1996 Sep 1;88(5):1525-41. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8781407 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Neonatal platelet physiology and implications for transfusion.Platelets. 2022 Jan 2;33(1):14-22. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2021.1962837. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Platelets. 2022. PMID: 34392772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced platelet function in preterm neonates compared with term neonates.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022 Aug 1;6(5):e12751. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12751. eCollection 2022 Jul. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35928524 Free PMC article.
-
Why might cord blood be a better source of platelets for transfusion to neonates?Blood Transfus. 2024 Jul 27;22(4):292-302. doi: 10.2450/BloodTransfus.566. Blood Transfus. 2024. PMID: 38557319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary hemostasis in fetal growth restricted neonates studied via PFA-100 in cord blood samples.Front Pediatr. 2022 Sep 8;10:946932. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.946932. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36160789 Free PMC article.
-
Current Controversy on Platelets and Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure in Preterm Infants.Front Pediatr. 2021 Feb 25;9:612242. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.612242. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33718298 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous