The role of histidine residues in modulation of the rat P2X(2) purinoceptor by zinc and pH
- PMID: 11882669
- PMCID: PMC2290168
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013244
The role of histidine residues in modulation of the rat P2X(2) purinoceptor by zinc and pH
Abstract
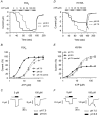
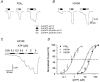
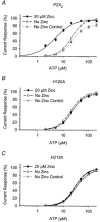
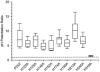
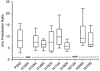
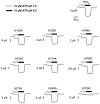
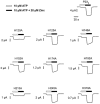
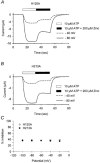
P2X(2) receptor currents are potentiated by acidic pH and zinc. To identify residues necessary for proton and zinc modulation, alanines were singly substituted for each of the nine histidines in the extracellular domain of the rat P2X(2) receptor. Wild-type and mutant receptors were expressed in Xenopus oocytes and analysed with two-electrode voltage clamp. All mutations caused less than a 2-fold change in the EC(50) of the ATP concentration-response relation. Decreasing the extracellular pH from 7.5 to 6.5 potentiated the responses to 10 microM ATP of wild-type P2X(2) and eight mutant receptors more than 4-fold, but the response of the mutant receptor H319A was potentiated only 1.4-fold. The H319A mutation greatly attenuated the maximal potentiation that could be produced by a drop in pH, shifted the pK(a) (-log of dissociation constant) of the potentiation to a more basic pH as compared with P2X(2) and revealed a substantial pH-dependent decrease in the maximum response with a pK(a) near 6.0. Substituting a lysine for H319 reduced the EC(50) for ATP 40-fold. Zinc (20 microM) potentiated the responses to 10 microM ATP of wild-type P2X(2) and seven histidine mutants by approximately 8-fold but had virtually no effect on the responses of two mutants, H120A and H213A. Neither H120A nor H213A removed the voltage-independent inhibition caused by high concentrations of zinc. The observation that different mutations selectively eliminated pH or zinc potentiation implies that there are two independent sites of action, even though the mechanisms of pH and zinc potentiation appear similar.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extracellular histidine residues identify common structural determinants in the copper/zinc P2X2 receptor modulation.J Neurochem. 2005 Oct;95(2):499-512. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03387.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 16190872
-
Mutational analysis of the conserved cysteines of the rat P2X2 purinoceptor.J Neurosci. 2002 May 15;22(10):3873-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-10-03873.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12019306 Free PMC article.
-
Differential role of extracellular histidines in copper, zinc, magnesium and proton modulation of the P2X7 purinergic receptor.J Neurochem. 2007 Apr;101(1):17-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04343.x. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17394459
-
Expression level dependent changes in the properties of P2X2 receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Mar;44(3):403-12. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00406-9. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12604087
-
Allosteric modulation of native cochlear P2X receptors: insights from comparison with recombinant P2X2 receptors.Audiol Neurootol. 2003 May-Jun;8(3):115-28. doi: 10.1159/000069478. Audiol Neurootol. 2003. PMID: 12679623
Cited by
-
Pharmacology of P2X channels.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):513-37. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0070-9. Epub 2006 Apr 29. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16649055 Review.
-
Identification of the amino acid residues in the extracellular domain of rat P2X(7) receptor involved in functional inhibition by acidic pH.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan;156(1):135-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00002.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19068080 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Type-Specific Expression of Purinergic P2X Receptors in the Hypothalamus.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 22;26(11):5007. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115007. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extended pharmacological profiles of rat P2Y2 and rat P2Y4 receptors and their sensitivity to extracellular H+ and Zn2+ ions.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Dec;140(7):1177-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705544. Epub 2003 Oct 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14581177 Free PMC article.
-
Structural interpretation of P2X receptor mutagenesis studies on drug action.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Nov;161(5):961-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00728.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20977449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acuna-Castillo C, Morales B, Huidobro-Toro JP. Zinc and copper modulate differentially the P2X4 receptor. Journal of Neurochemistry. 2000;74:1529–1537. - PubMed
-
- Alberty RA. Effect of pH and metal ion concentration on the equilibrium hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate to adenosine diphosphate. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1968;243:1337–1343. - PubMed
-
- Brake AJ, Julius D. Signaling by extracellular nucleotides. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 1996;12:519–541. - PubMed
-
- Brake AJ, Wagenbach MJ, Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994;371:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Brooks SP, Storey KB. Bound and determined: a computer program for making buffers of defined ion concentrations. Analytical Biochemistry. 1992;201:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

