Skeletal muscle L-type Ca(2+) current modulation in gamma1-deficient and wildtype murine myotubes by the gamma1 subunit and cAMP
- PMID: 11882678
- PMCID: PMC2290155
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.012745
Skeletal muscle L-type Ca(2+) current modulation in gamma1-deficient and wildtype murine myotubes by the gamma1 subunit and cAMP
Abstract
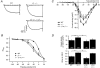
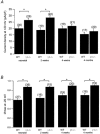
Modulation of the steady-state inactivation and current amplitude by the gamma1 subunit of the murine skeletal muscle L-type Ca(2+) channel were investigated using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. Transient expression of the gamma1 subunit, but not of the gamma2 (stargazin) protein, in primary cultured myotubes from gamma1-deficient mice shifted the steady-state inactivation approximately -15 mV, thereby restoring wildtype (WT) steady-state inactivation and current amplitude. The increased Ca(2+) current amplitude in gamma1-deficient cells was abolished in myotubes from animals of 4 weeks and older whereas the positive shift in steady-state inactivation was independent of mouse age. Raising intracellular cAMP levels using the membrane-permeant analogue 8-Br-cAMP led to an increase in Ca(2+) current amplitude in WT cells to the level in gamma1-deficient myotubes. There was no effect on the current amplitude in gamma1-deficient cells or on the steady-state inactivation in either genotype. Rp-cAMPS, a competitive inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, had no effect on the WT Ca(2+) current amplitude and steady-state inactivation, but diminished the current amplitude in gamma1-deficient myotubes without affecting the steady-state inactivation in these cells. These data show that the increased Ca(2+) influx in myotubes lacking the gamma1 subunit, due to right-shifted steady-state inactivation and increased L-type Ca(2+) current amplitude, is determined by the gamma1 subunit. The effect on current amplitude depends on the age of the mice and its cAMP-dependent modulation appears to be controlled by the gamma1 subunit.
Figures


References
-
- Ahern CA, Powers PA, Biddlecome GH, Roethe L, Vallejo P, Mortenson L, Strube C, Campbell KP, Coronado R, Gregg RG. Modulation of L-type Ca2+ current but not activation of Ca2+ release by the gamma1 subunit of the dihydropyridine receptor of skeletal muscle. BioMedCentral Physiology. 2001;1:8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berthier C, Powers PA, Gregg RG, Coronado R, Strube C. Absence of regulation of skeletal muscle T-type calcium channel by dihydropyridine receptor subunits in vivo. Biophysical Journal. 2001;80:546.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

