Coxsackievirus B3 replication is reduced by inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway
- PMID: 11884562
- PMCID: PMC136021
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3365-3373.2002
Coxsackievirus B3 replication is reduced by inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway
Abstract
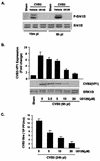
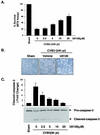
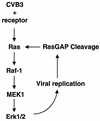
Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) is the most common human pathogen for viral myocarditis. We have previously shown that the signaling protein p21(ras) GTPase-activating protein (RasGAP) is cleaved and that mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) ERK1/2 are activated in the late phase of CVB3 infection. However, the role of intracellular signaling pathways in CVB3-mediated myocarditis and the relative advantages of such pathways to host or virus remain largely unclear. In this study we extended our prior studies by examining the interaction between CVB3 replication and intracellular signaling pathways in HeLa cells. We observed that CVB3 infection induced a biphasic activation of ERK1/2, early transient activation versus late sustained activation, which were regulated by different mechanisms. Infection by UV-irradiated, inactivated virus capable of receptor binding and endocytosis triggered early ERK1/2 activation, but was insufficient to trigger late ERK1/2 activation. By using a general caspase inhibitor (zVAD.fmk) we further demonstrated that late ERK1/2 activation was not a result of CVB3-mediated caspase cleavage. Treatment of cells with U0126, a selective inhibitor of MAPK kinase (MEK), significantly inhibited CVB3 progeny release and decreased virus protein production. Furthermore, inhibition of ERK1/2 activation circumvented CVB3-induced apoptosis and viral protease-mediated RasGAP cleavage. Taken together, these data suggest that ERK1/2 activation is important for CVB3 replication and contributes to virus-mediated changes in host cells. Our findings demonstrate coxsackievirus takeover of a particular host signaling mechanism and uncover a prospective approach to stymie virus spread and preserve myocardial integrity.
Figures



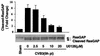
References
-
- Badorff, C., G. H. Lee, B. J. Lamphear, M. E. Martone, K. P. Campbell, R. E. Rhoads, and K. U. Knowlton. 1999. Enteroviral protease 2A cleaves dystrophin: evidence of cytoskeletal disruption in an acquired cardiomyopathy. Nat. Med. 5:320-326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

