Activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory protein p12(I)
- PMID: 11884573
- PMCID: PMC136046
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3493-3501.2002
Activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory protein p12(I)
Abstract
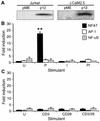
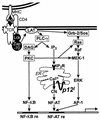
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is the agent of an aggressive malignancy of CD4(+) T lymphocytes, called adult T-cell lymphoma/leukemia, and is associated with numerous immune-mediated diseases. To establish infection, HTLV-1 must activate targeted T cells during early stages of infection. We recently demonstrated that the HTLV-1 accessory protein p12(I) is critical for persistent infection in vivo and for viral infectivity in quiescent primary lymphocytes, suggesting a role for p12(I) in lymphocyte activation. To test whether p12(I) modulates signaling pathways required for T-lymphocyte activation, we examined AP-1-, NF-kappaB-, and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)-driven reporter gene activity in p12(I)-expressing Jurkat T cells compared to vector-transfected control cells. HTLV-1 p12(I) specifically induced NFAT-mediated transcription approximately 20-fold in synergy with the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, but did not influence AP-1- or NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Inhibition of calcium-dependent signals by cyclosporin A, BAPTA-AM [glycine, N,N'-1,2-ethanediylbis(oxy-2,1-phenylene)-bis-N-2-(acetyloxy)methoxy-2-oxoethyl]-[bis(acetyloxy)methyl ester], and a dominant negative mutant of NFAT2 abolished the p12(I)-mediated activation of NFAT-dependent transcription. In contrast, inhibition of phospholipase C-gamma and LAT (linker for activation of T cells) did not affect p12(I)-induced NFAT activity. Importantly, p12(I) functionally substituted for thapsigargin, which selectively depletes intracellular calcium stores. Our data are the first to demonstrate a role for HTLV-1 p12(I) in calcium-dependent activation of NFAT-mediated transcription in lymphoid cells. We propose a novel mechanism by which HTLV-1, a virus associated with lymphoproliferative disease, dysregulates common T-cell activation pathways critical for the virus to establish persistent infection.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 p12(I) expression increases cytoplasmic calcium to enhance the activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells.J Virol. 2002 Oct;76(20):10374-82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10374-10382.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12239314 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 p12I enhances interleukin-2 production during T-cell activation.J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(20):11027-39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.20.11027-11039.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14512551 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved calcineurin-binding motif in human T lymphotropic virus type 1 p12I functions to modulate nuclear factor of activated T cell activation.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 2;278(18):15550-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210210200. Epub 2003 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12601010
-
Critical role of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory proteins in viral replication and pathogenesis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002 Sep;66(3):396-406, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.66.3.396-406.2002. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12208996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of accessory proteins of HTLV-1 in viral replication, T cell activation, and cellular gene expression.Front Biosci. 2004 Sep 1;9:2556-76. doi: 10.2741/1417. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15358581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel one-class SVM based negative data sampling method for reconstructing proteome-wide HTLV-human protein interaction networks.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 26;5:8034. doi: 10.1038/srep08034. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25620466 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell control by human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type 1.Int J Hematol. 2003 Nov;78(4):280-96. doi: 10.1007/BF02983552. Int J Hematol. 2003. PMID: 14686485 Review.
-
Converging strategies in expression of human complex retroviruses.Viruses. 2011 Aug;3(8):1395-414. doi: 10.3390/v3081395. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Palmitoylation and p8-mediated human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 transmission.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(4):2319-22. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03444-13. Epub 2013 Nov 27. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24284316 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 non-structural proteins: Requirements for latent infection.Cancer Sci. 2013 Aug;104(8):983-8. doi: 10.1111/cas.12190. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23651172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman, A., N. Isakov, and G. Baier. 2000. Protein kinase C theta: a new essential superstar on the T-cell stage. Immunol. Today 21:567-573. - PubMed
-
- Berneman, Z. N., R. B. Gartenhaus, M. S. Reitz, W. A. Blattner, A. Manns, B. Hanchard, O. Ikehara, R. C. Gallo, and M. E. Klotman. 1992. Expression of alternatively spliced human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 pX mRNA in infected cell lines and in primary uncultured cells from patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and healthy carriers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:3005-3009. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

