Ctr9, Rtf1, and Leo1 are components of the Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex
- PMID: 11884586
- PMCID: PMC133696
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.1971-1980.2002
Ctr9, Rtf1, and Leo1 are components of the Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex
Abstract
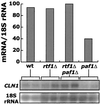
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1-RNA polymerase II (Pol II) complex is biochemically and functionally distinct from the Srb-mediator form of Pol II holoenzyme and is required for full expression of a subset of genes. In this work we have used tandem affinity purification tags to isolate the Paf1 complex and mass spectrometry to identify additional components. We have established that Ctr9, Rtf1, and Leo1 are factors that associate with Paf1, Cdc73, and Pol II, but not with the Srb-mediator. Deletion of either PAF1 or CTR9 leads to similar severe pleiotropic phenotypes, which are unaltered when the two mutations are combined. In contrast, we found that deletion of LEO1 or RTF1 leads to few obvious phenotypes, although mutation of RTF1 suppresses mutations in TATA-binding protein, alters transcriptional start sites, and affects elongation. Remarkably, deletion of LEO1 or RTF1 suppresses many paf1Delta phenotypes. In particular, an rtf1Delta paf1Delta double mutant grew faster, was less temperature sensitive, and was more resistant to caffeine and hydroxyurea than a paf1Delta single mutant. In addition, expression of the G(1) cyclin CLN1, reduced nearly threefold in paf1Delta, is restored to wild-type levels in the rtf1Delta paf1Delta double mutant. We suggest that lack of Paf1 results in a defective complex and a block in transcription, which is relieved by removal of Leo1 or Rtf1.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Separation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1 complex from RNA polymerase II results in changes in its subnuclear localization.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Jan;4(1):209-20. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.1.209-220.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 15643076 Free PMC article.
-
Direct interactions between the Paf1 complex and a cleavage and polyadenylation factor are revealed by dissociation of Paf1 from RNA polymerase II.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Jul;7(7):1158-67. doi: 10.1128/EC.00434-07. Epub 2008 May 9. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18469135 Free PMC article.
-
Paf1 and Ctr9, core components of the PAF1 complex, maintain low levels of telomeric repeat containing RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 25;46(2):621-634. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1131. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29145644 Free PMC article.
-
The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May-Jun;1799(5-6):379-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20060942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purification of yeast RNA polymerase II holoenzymes.Methods Enzymol. 1996;273:176-84. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)73018-5. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 8791611 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Evidence that Spt2/Sin1, an HMG-like factor, plays roles in transcription elongation, chromatin structure, and genome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(4):1496-509. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.4.1496-1509.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16449659 Free PMC article.
-
The distribution of active RNA polymerase II along the transcribed region is gene-specific and controlled by elongation factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Aug;38(14):4651-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq215. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20385590 Free PMC article.
-
The HRPT2 tumor suppressor gene product parafibromin associates with human PAF1 and RNA polymerase II.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;25(12):5052-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.12.5052-5060.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15923622 Free PMC article.
-
Mutants of the Paf1 complex alter phenotypic expression of the yeast prion [PSI+].Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Apr;20(8):2229-41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0813. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19225160 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanism related to the yeast transcriptional regulator Paf1c is required for expression of the Arabidopsis FLC/MAF MADS box gene family.Plant Cell. 2004 Nov;16(11):2940-53. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026062. Epub 2004 Oct 7. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15472079 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
