Convergence of multiple signaling cascades at glycogen synthase kinase 3: Edg receptor-mediated phosphorylation and inactivation by lysophosphatidic acid through a protein kinase C-dependent intracellular pathway
- PMID: 11884598
- PMCID: PMC133668
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2099-2110.2002
Convergence of multiple signaling cascades at glycogen synthase kinase 3: Edg receptor-mediated phosphorylation and inactivation by lysophosphatidic acid through a protein kinase C-dependent intracellular pathway
Abstract
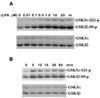
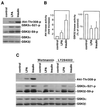
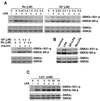
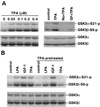
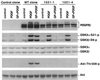
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a natural phospholipid with multiple biological functions. We show here that LPA induces phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3), a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase. The effect of LPA can be reconstituted by expression of Edg-4 or Edg-7 in cells lacking LPA responses. Compared to insulin, LPA stimulates only modest phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent activation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) that does not correlate with the magnitude of GSK-3 phosphorylation induced by LPA. PI3K inhibitors block insulin- but not LPA-induced GSK-3 phosphorylation. In contrast, the effect of LPA, but not that of insulin or platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), is sensitive to protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors. Downregulation of endogenous PKC activity selectively reduces LPA-mediated GSK-3 phosphorylation. Furthermore, several PKC isotypes phosphorylate GSK-3 in vitro and in vivo. To confirm a specific role for PKC in regulation of GSK-3, we further studied signaling properties of PDGF receptor beta subunit (PDGFRbeta) in HEK293 cells lacking endogenous PDGF receptors. In clones expressing a PDGFRbeta mutant wherein the residues that couple to PI3K and other signaling functions are mutated with the link to phospholipase Cgamma (PLCgamma) left intact, PDGF is fully capable of stimulating GSK-3 phosphorylation. The process is sensitive to PKC inhibitors in contrast to the response through the wild-type PDGFRbeta. Therefore, growth factors, such as PDGF, which control GSK-3 mainly through the PI3K-PKB/Akt module, possess the ability to regulate GSK-3 through an alternative, redundant PLCgamma-PKC pathway. LPA and potentially other natural ligands primarily utilize a PKC-dependent pathway to modulate GSK-3.
Figures

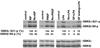


References
-
- Bellacosa, A., J. R. Testa, S. P. Staal, and P. N. Tsichlis. 1991. A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine-threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region. Science 254:271-274. - PubMed
-
- Bonni, A., A. Brunet, A. E. West, S. R. Datta, M. A. Takasu, and M. E. Greenberg. 1999. Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and independent mechanisms. Science 286:1358-1362. - PubMed
-
- Chen, E. Y., N. M. Mazure, J. A. Cooper, and A. J. Giaccia. 2001. Hypoxia activates a platelet-derived growth factor receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway that results in glycogen synthase kinase-3 inactivation. Cancer Res. 61:2429-2433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
