Dnmt1 overexpression causes genomic hypermethylation, loss of imprinting, and embryonic lethality
- PMID: 11884600
- PMCID: PMC133685
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2124-2135.2002
Dnmt1 overexpression causes genomic hypermethylation, loss of imprinting, and embryonic lethality
Abstract
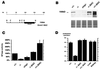
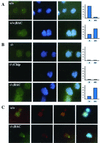
Biallelic expression of Igf2 is frequently seen in cancers because Igf2 functions as a survival factor. In many tumors the activation of Igf2 expression has been correlated with de novo methylation of the imprinted region. We have compared the intrinsic susceptibilities of the imprinted region of Igf2 and H19, other imprinted genes, bulk genomic DNA, and repetitive retroviral sequences to Dnmt1 overexpression. At low Dnmt1 methyltransferase levels repetitive retroviral elements were methylated and silenced. The nonmethylated imprinted region of Igf2 and H19 was resistant to methylation at low Dnmt1 levels but became fully methylated when Dnmt1 was overexpressed from a bacterial artificial chromosome transgene. Methylation caused the activation of the silent Igf2 allele in wild-type and Dnmt1 knockout cells, leading to biallelic Igf2 expression. In contrast, the imprinted genes Igf2r, Peg3, Snrpn, and Grf1 were completely resistant to de novo methylation, even when Dnmt1 was overexpressed. Therefore, the intrinsic difference between the imprinted region of Igf2 and H19 and of other imprinted genes to postzygotic de novo methylation may be the molecular basis for the frequently observed de novo methylation and upregulation of Igf2 in neoplastic cells and tumors. Injection of Dnmt1-overexpressing embryonic stem cells in diploid or tetraploid blastocysts resulted in lethality of the embryo, which resembled embryonic lethality caused by Dnmt1 deficiency.
Figures
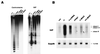
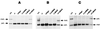



References
-
- Bartolomei, M. S., A. L. Webber, M. E. Brunkow, and S. M. Tilghman. 1993. Epigenetic mechanisms underlying the imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Genes Dev. 7:1663-1673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
