Identification of a novel hypoxia-inducible factor 1-responsive gene, RTP801, involved in apoptosis
- PMID: 11884613
- PMCID: PMC133671
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2283-2293.2002
Identification of a novel hypoxia-inducible factor 1-responsive gene, RTP801, involved in apoptosis
Abstract
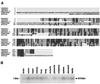
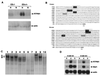
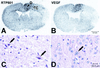
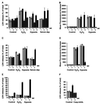
Hypoxia is an important factor that elicits numerous physiological and pathological responses. One of the major gene expression programs triggered by hypoxia is mediated through hypoxia-responsive transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1). Here, we report the identification and cloning of a novel HIF-1-responsive gene, designated RTP801. Its strong up-regulation by hypoxia was detected both in vitro and in vivo in an animal model of ischemic stroke. When induced from a tetracycline-repressible promoter, RTP801 protected MCF7 and PC12 cells from hypoxia in glucose-free medium and from H(2)O(2)-triggered apoptosis via a dramatic reduction in the generation of reactive oxygen species. However, expression of RTP801 appeared toxic for nondividing neuron-like PC12 cells and increased their sensitivity to ischemic injury and oxidative stress. Liposomal delivery of RTP801 cDNA to mouse lungs also resulted in massive cell death. Thus, the biological effect of RTP801 overexpression depends on the cell context and may be either protecting or detrimental for cells under conditions of oxidative or ischemic stresses. Altogether, the data suggest a complex type of involvement of RTP801 in the pathogenesis of ischemic diseases.
Figures


References
-
- An, W. G., M. Kanekal, M. C. Simon, E. Maltepe, M. V. Blagosklonny, and L. M. Neckers. 1998. Stabilization of wild-type p53 by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Nature 392:405-408. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron, M., J. M. Gidday, A. Y. Yu, G. L. Semenza, D. M. Ferriero, and F. R. Sharp. 2000. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in hypoxia-induced ischemic tolerance in neonatal rat brain. Ann. Neurol. 48:285-296. - PubMed
-
- Brand, K. A., and U. Hermfisse. 1997. Aerobic glycolysis by proliferating cells: a protective strategy against reactive oxygen species. FASEB J. 11:388-395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
