Requirement of RAD5 and MMS2 for postreplication repair of UV-damaged DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 11884624
- PMCID: PMC133702
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2419-2426.2002
Requirement of RAD5 and MMS2 for postreplication repair of UV-damaged DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
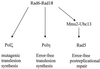
UV lesions in the template strand block the DNA replication machinery. Genetic studies of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae have indicated the requirement of the Rad6-Rad18 complex, which contains ubiquitin-conjugating and DNA-binding activities, in the error-free and mutagenic modes of damage bypass. Here, we examine the contributions of the REV3, RAD30, RAD5, and MMS2 genes, all of which belong to the RAD6 epistasis group, to the postreplication repair of UV-damaged DNA. Discontinuities, which are formed in DNA strands synthesized from UV-damaged templates, are not repaired in the rad5Delta and mms2Delta mutants, thus indicating the requirement of the Rad5 protein and the Mms2-Ubc13 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex in this repair process. Some discontinuities accumulate in the absence of RAD30-encoded DNA polymerase eta (Poleta) but not in the absence of REV3-encoded DNA Polzeta. We concluded that replication through UV lesions in yeast is mediated by at least three separate Rad6-Rad18-dependent pathways, which include mutagenic translesion synthesis by Polzeta, error-free translesion synthesis by Poleta, and postreplication repair of discontinuities by a Rad5-dependent pathway. We suggest that newly synthesized DNA possessing discontinuities is restored to full size by a "copy choice" type of DNA synthesis which requires Rad5, a DNA-dependent ATPase, and also PCNA and Poldelta. The possible roles of the Rad6-Rad18 and the Mms2-Ubc13 enzyme complexes in Rad5-dependent damage bypass are discussed.
Figures
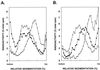
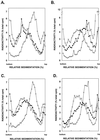
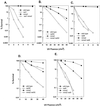
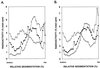
References
-
- Armstrong, J. D., D. N. Chadee, and B. A. Kunz. 1994. Roles of the yeast RAD18 and RAD52 DNA repair genes in UV mutagenesis. Mutat. Res. 315:281-293. - PubMed
-
- Bailly, V., J. Lamb, P. Sung, S. Prakash, and L. Prakash. 1994. Specific complex formation between yeast RAD6 and RAD18 proteins: a potential mechanism for targeting RAD6 ubiquitin-conjugating activity to DNA damage sites. Genes Dev. 8:811-820. - PubMed
-
- Bailly, V., S. Lauder, S. Prakash, and L. Prakash. 1997. Yeast DNA repair proteins Rad6 and Rad18 form a heterodimer that has ubiquitin conjugating, DNA binding, and ATP hydrolytic activities. J. Biol. Chem. 272:23360-23365. - PubMed
-
- Cassier-Chauvat, C., and F. Fabre. 1991. A similar defect in UV-induced mutagenesis conferred by the rad6 and rad18 mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat. Res. 254:247-253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
