The putative plasma membrane Na(+)/H(+) antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na(+) transport in plants
- PMID: 11884687
- PMCID: PMC152925
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010371
The putative plasma membrane Na(+)/H(+) antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na(+) transport in plants
Abstract
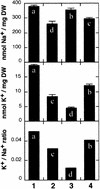
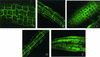
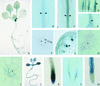
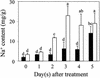
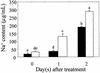
The salt tolerance locus SOS1 from Arabidopsis has been shown to encode a putative plasma membrane Na(+)/H(+) antiporter. In this study, we examined the tissue-specific pattern of gene expression as well as the Na(+) transport activity and subcellular localization of SOS1. When expressed in a yeast mutant deficient in endogenous Na(+) transporters, SOS1 was able to reduce Na(+) accumulation and improve salt tolerance of the mutant cells. Confocal imaging of a SOS1-green fluorescent protein fusion protein in transgenic Arabidopsis plants indicated that SOS1 is localized in the plasma membrane. Analysis of SOS1 promoter-beta-glucuronidase transgenic Arabidopsis plants revealed preferential expression of SOS1 in epidermal cells at the root tip and in parenchyma cells at the xylem/symplast boundary of roots, stems, and leaves. Under mild salt stress (25 mM NaCl), sos1 mutant shoot accumulated less Na(+) than did the wild-type shoot. However, under severe salt stress (100 mM NaCl), sos1 mutant plants accumulated more Na(+) than did the wild type. There also was greater Na(+) content in the xylem sap of sos1 mutant plants exposed to 100 mM NaCl. These results suggest that SOS1 is critical for controlling long-distance Na(+) transport from root to shoot. We present a model in which SOS1 functions in retrieving Na(+) from the xylem stream under severe salt stress, whereas under mild salt stress it may function in loading Na(+) into the xylem.
Figures




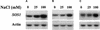
References
-
- Amtmann, A., and Sanders, D. (1999). Mechanisms of Na+ uptake by plant cells. Adv. Bot. Res. 29, 75–112.
-
- Apse, M.P., Aharon, G.S., Snedden, W.A., and Blumwald, E. (1999). Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285, 1256–1258. - PubMed
-
- Bañuelos, M.A., Sychrová, H., Bleykasten-Grosshans, C., Souciet, J.L., and Potier, S. (1998). The Nha1 antiporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediates sodium and potassium efflux. Microbiology 144, 2749–2758. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold, N., Ellis, J., and Pelletier, G. (1993). In planta Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis thaliana plants. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 316, 1194–1199.
-
- Blumwald, E., Aharon, G.S., and Apse, M.P. (2000). Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1465, 140–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

