The Wilms' tumor gene Wt1 is required for normal development of the retina
- PMID: 11889045
- PMCID: PMC125354
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.6.1398
The Wilms' tumor gene Wt1 is required for normal development of the retina
Abstract
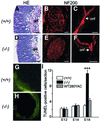
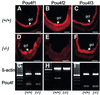
The Wilms' tumor gene Wt1 is known for its important functions during genitourinary and mesothelial formation. Here we show that Wt1 is necessary for neuronal development in the vertebrate retina. Mouse embryos with targeted disruption of Wt1 exhibit remarkably thinner retinas than age-matched wild-type animals. A large fraction of retinal ganglion cells is lost by apoptosis, and the growth of optic nerve fibers is severely disturbed. Strikingly, expression of the class IV POU-domain transcription factor Pou4f2 (formerly Brn-3b), which is critical for the survival of most retinal ganglion cells, is lost in Wt1(-/-) retinas. Forced expression of Wt1 in cultured cells causes an up-regulation of Pou4f2 mRNA. Moreover, the Wt1(-KTS) splice variant can activate a reporter construct carrying 5'-regulatory sequences of the human POU4F2. The lack of Pou4f2 and the ocular defects in Wt1(-/-) embryos are rescued by transgenic expression of a 280 kb yeast artificial chromosome carrying the human WT1 gene. Taken together, our findings demonstrate a continuous requirement for Wt1 in normal retina formation with a critical role in Pou4f2-dependent ganglion cell differentiation.
Figures




References
-
- Armstrong J.F., Pritchard-Jones,K., Bickmore,W.A., Hastie,N.D. and Bard,J.B. (1993) The expression of the Wilms’ tumor gene, WT1, in the developing mammalian embryo. Mech. Dev., 40, 85–97. - PubMed
-
- Bennington J. and Beckwith,J. (1975) Tumors in the kidney, renal pelvis and ureter. In Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Series 2, fascile 12. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC.
-
- Bickmore W.A. and Hastie,N.D. (1989) Aniridia, Wilms’ tumor and human chromosome 11. Ophthalmic Paediatr. Genet., 10, 229–248. - PubMed
-
- Braissant O. and Wahli,W. (1998) A simplified in situ hybridization protocol using non-radioactively labeled probes to detect abundant and rare mRNAs on tissue sections. Biochemica, 1, 10–16.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

