A ligand for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells
- PMID: 11889080
- PMCID: PMC1773180
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.50.4.563
A ligand for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells
Abstract
Background and aims: Induction of apoptosis of cancer cells through ligands of nuclear hormone receptors (NHRs) is a new approach in cancer therapy. Recently, one of the NHRs, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), has been shown to influence cell growth in certain cancer cells although its effect on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been analysed.
Methods: Experiments were conducted using three human liver cancer cell lines, PLC/PRF/5, Hep G2 and HuH-7, in vitro. These cells were exposed to troglitazone, a synthetic ligand for PPARgamma, and the effects on cell growth were analysed.
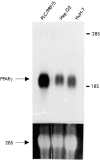
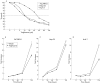
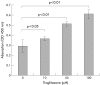
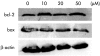
Results: Expression of PPARgamma mRNA was detected in all three liver cancer cell lines. Activation of PPARgamma by troglitazone caused a marked growth inhibition in a dose dependent manner in three hepatoma cell lines. The DNA fragmentation ELISA assay and Hoechst 33258 staining revealed that the growth inhibitory effect by adding troglitazone was due to apoptosis of PLC/PRF/5, which strongly expressed PPARgamma. Troglitazone also induced activation of the cell death protease, caspase 3, but not caspase 8, in PLC/PRF/5 cells. However, expression levels of antiapoptotic factor bcl-2 and apoptosis inducing factor bax were not affected.
Conclusion: Our study showed that PPARgamma was expressed in human liver cancer cells and that the ligand for PPARgamma, troglitazone, inhibited the growth of these cells by inducing apoptosis through caspase 3 activation, indicating that troglitazone could be potentially useful as an apoptosis inducer for the treatment of HCC.
Figures

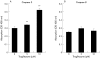
Similar articles
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand troglitazone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines.Cancer. 2002 Nov 15;95(10):2243-51. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10906. Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12412180
-
Involvement of p21(WAF1/Cip1), p27(Kip1), and p18(INK4c) in troglitazone-induced cell-cycle arrest in human hepatoma cell lines.Hepatology. 2001 May;33(5):1087-97. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.24024. Hepatology. 2001. PMID: 11343236
-
Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma by troglitazone inhibits cell growth through the increase of p27KiP1 in human. Pancreatic carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2000 Oct 1;60(19):5558-64. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 11034103
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPargamma) as a novel target for prostate cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2002 May;20(2):195-200. doi: 10.1023/a:1015670126203. Invest New Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12099579 Review.
-
Toxicological consequences of altered peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) expression in the liver: insights from models of obesity and type 2 diabetes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2002 Jan 1;63(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00817-6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11754868 Review.
Cited by
-
Study on cow ghee versus soybean oil on 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)-anthracene induced mammary carcinogenesis & expression of cyclooxygenase-2 & peroxisome proliferators activated receptor-γ in rats.Indian J Med Res. 2011 May;133(5):497-503. Indian J Med Res. 2011. PMID: 21623034 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of PPARγ natural agonists in liver diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Mar;24(5):2736-2748. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15028. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32031298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPAR Ligands for Cancer Chemoprevention.PPAR Res. 2008;2008:548919. doi: 10.1155/2008/548919. PPAR Res. 2008. PMID: 18483618 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of PPARs in Cancer.PPAR Res. 2008;2008:102737. doi: 10.1155/2008/102737. PPAR Res. 2008. PMID: 18584037 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ activation by troglitazone enhances human lung cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via autophagy flux.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):26819-26831. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15819. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28460464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Omata M. Current perspectives on hepatocellular carcinoma in Oriental and African countries compared to developed western countries. Dig Dis Sci 1987;5:97–115. - PubMed
-
- Okuda K. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Hepatology 1992;15:948–63. - PubMed
-
- Warrell RP Jr, Frankel SR, Miller WH Jr, et al. Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). N Engl J Med 1991;324:1385–93. - PubMed
-
- Tallman MS. Differentiating therapy with all-trans retinoic acid in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1996;10(suppl 1):S12–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
