Effect of different concentrations of H-NS protein on chromosome replication and the cell cycle in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 11889089
- PMCID: PMC134913
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.7.1843-1850.2002
Effect of different concentrations of H-NS protein on chromosome replication and the cell cycle in Escherichia coli
Abstract
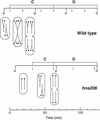
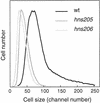
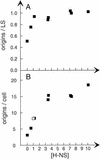
Flow cytometric analysis showed that the hns205 and hns206 mutants, lacking the abundant nucleoid-associated protein H-NS, have decreased origin concentration, as well as a low number of origins per cell (ploidy). The most striking observation was that the low ploidy was due to a very short replication time, e.g., at 30 degrees C it was halved compared to that of the hns(+) strain. The decreased origin concentration was not caused by a decreased dnaA gene expression, and the hns206 mutant had normal DnaA protein concentrations. The replication phenotypes of the hns206 mutant were independent of RpoS. Cells overproducing H-NS from a LacI-controlled plasmid had a normal origin concentration, indicating that H-NS is not controlling initiation. A wild-type H-NS concentration is, however, required to obtain a wild-type origin concentration, since cells with an intermediate H-NS concentration had an intermediate origin concentration. Two lines of evidence point to an indirect effect of H-NS on initiation. First, H-NS did not show high-affinity binding to any part of oriC, and H-NS had no effect on transcription entering oriC from the mioC promoter. Second, in a shift experiment with the hns206 mutant, when H-NS protein was induced to wild-type levels within 10 min, it took more than one generation before the origin concentration started to increase.
Figures

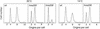


References
-
- Atlung, T., and H. Ingmer. 1997. H-NS: a modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 24:7-17. - PubMed
-
- Atlung, T., A. Nielsen, L. J. Rasmussen, L. J. Nellemann, and F. Holm. 1991. A versatile method for integration of genes and gene fusions into the λ attachment site of Escherichia coli. Gene 107:11-17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

