Characterization of an ADP-ribosyltransferase toxin (AexT) from Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida
- PMID: 11889090
- PMCID: PMC134929
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.7.1851-1858.2002
Characterization of an ADP-ribosyltransferase toxin (AexT) from Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida
Abstract
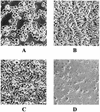
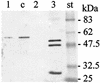
An ADP-ribosylating toxin named Aeromonas salmonicida exoenzyme T (AexT) in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, the etiological agent of furunculosis in fish, was characterized. Gene aexT, encoding toxin AexT, was cloned and characterized by sequence analysis. AexT shows significant sequence similarity to the ExoS and ExoT exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and to the YopE cytotoxin of different Yersinia species. The aexT gene was detected in all of the 12 A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida strains tested but was absent from all other Aeromonas species. Recombinant AexT produced in Escherichia coli possesses enzymatic ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Monospecific polyclonal antibodies directed against purified recombinant AexT detected the toxin produced by A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida and cross-reacted with ExoS and ExoT of P. aeruginosa. AexT toxin could be detected in a wild type (wt) strain of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida freshly isolated from a fish with furunculosis; however, its expression required contact with RTG-2 rainbow trout gonad cells. Under these conditions, the AexT protein was found to be intracellular or tightly cell associated. No AexT was found when A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida was incubated in cell culture medium in the absence of RTG-2 cells. Upon infection with wt A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, the fish gonad RTG-2 cells rapidly underwent significant morphological changes. These changes were demonstrated to constitute cell rounding, which accompanied induction of production of AexT and which led to cell lysis after extended incubation. An aexT mutant which was constructed from the wt strain with an insertionally inactivated aexT gene by allelic exchange had no toxic effect on RTG-2 cells and was devoid of AexT production. Hence AexT is directly involved in the toxicity of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida for RTG-2 fish cells.
Figures


References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1999. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Belland, R. J., and T. J. Trust. 1988. DNA:DNA reassociation analysis of Aeromonas salmonicida. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134:307-315. - PubMed
-
- Bullock, W. O., J. M. Fernandez, and J. M. Short. 1987. XL1-Blue: a high efficiency plasmid transforming recA Escherichia coli strain with beta-galactosidase selection. BioTechniques 5:376-378.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

