Molecular analysis of the gene encoding a novel chitin-binding protease from Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 and its role in the chitinolytic system
- PMID: 11889092
- PMCID: PMC134925
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.7.1865-1872.2002
Molecular analysis of the gene encoding a novel chitin-binding protease from Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 and its role in the chitinolytic system
Abstract
Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 secretes several proteins in response to chitin induction. We have found that one of these proteins, designated AprIV, is a novel chitin-binding protease involved in chitinolytic activity. The gene encoding AprIV (aprIV) was cloned in Escherichia coli. DNA sequencing analysis revealed that the open reading frame of aprIV encoded a protein of 547 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 57,104 Da. AprIV is a modular enzyme consisting of five domains: the signal sequence, the N-terminal proregion, the family A subtilase region, the polycystic kidney disease domain (PkdD), and the chitin-binding domain type 3 (ChtBD3). Expression plasmids coding for PkdD or both PkdD and ChtBD (PkdD-ChtBD) were constructed. The PkdD-ChtBD but not PkdD exhibited strong binding to alpha-chitin and beta-chitin. Western and Northern analyses demonstrated that aprIV was induced in the presence of N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylchitobiose, or chitin. Native AprIV was purified to homogeneity from Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 and characterized. The molecular mass of mature AprIV was estimated to be 44 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The optimum pH and temperature of AprIV were pH 11.5 and 35 degrees C, respectively, and even at 10 degrees C the enzyme showed 25% of the maximum activity. Pretreatment of native chitin with AprIV significantly promoted chitinase activity.
Figures
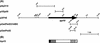
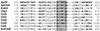

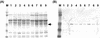




References
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brun, E., F. Moriaud, P. Gans, M. J. Blackledge, F. Barras, and D. Marion. 1997. Solution structure of the cellulose-binding domain of the endoglucanase Z secreted by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Biochemistry 36:16074-16086. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

