Differing roles for urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activator in collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 11891190
- PMCID: PMC1867189
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64914-0
Differing roles for urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activator in collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
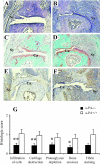
The plasminogen activators, urokinase PA (u-PA) and tissue-type PA (t-PA), are believed to play important roles in inflammatory cell infiltration, fibrin deposition, and joint destruction associated with rheumatoid arthritis; however, their precise roles in such processes, particularly u-PA, have yet to be defined. Using gene-deficient mice we examined the relative contribution of the PAs to the chronic systemic collagen-induced arthritis model. Based on clinical and histological assessments, u-PA-/- mice developed significantly milder disease and t-PA-/- mice more severe disease compared with the relevant wild-type mice. Fibrin deposition within joints paralleled disease severity and was particularly pronounced in t-PA-/- mice. Likewise, cytokine levels in the synovium reflected the severity of disease, with interleukin-1beta levels in particular being lower in u-PA-/- mice and increased in t-PA-/- mice. The antibody response to type II collagen was normal in both knockouts; however, T cells from u-PA-/- mice had a reduced proliferative response and produced less interferon-gamma on antigen stimulation in vitro. These results indicate that the major effect of u-PA in the collagen-induced arthritis model is deleterious, whereas that of t-PA is protective. Our data highlight the complexities of PA function, and suggest that approaches either to target u-PA or to enhance local t-PA activity in joints may be of therapeutic benefit in rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The plasminogen activator/plasmin system is essential for development of the joint inflammatory phase of collagen type II-induced arthritis.Am J Pathol. 2005 Mar;166(3):783-92. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62299-7. Am J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15743790 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen-dependent and -independent proteolytic activity of murine endothelioma cells with targeted inactivation of fibrinolytic genes.Thromb Haemost. 1997 Feb;77(2):362-7. Thromb Haemost. 1997. PMID: 9157597
-
The effect of tissue type-plasminogen activator deletion and associated fibrin(ogen) deposition on macrophage localization in peritoneal inflammation.Thromb Haemost. 2006 Apr;95(4):659-67. Thromb Haemost. 2006. PMID: 16601837
-
Influence of t-pA and u-PA on adipose tissue development in a murine model of diet-induced obesity.Thromb Haemost. 2002 Feb;87(2):306-10. Thromb Haemost. 2002. PMID: 11858492
-
Physiological consequences of loss of plasminogen activator gene function in mice.Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):419-24. doi: 10.1038/368419a0. Nature. 1994. PMID: 8133887
Cited by
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and arthritis progression: contrasting roles in systemic and monoarticular arthritis models.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R199. doi: 10.1186/ar3171. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20973954 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutics targeting the fibrinolytic system.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Mar;52(3):367-379. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0397-x. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32152451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibrin(ogen) exacerbates inflammatory joint disease through a mechanism linked to the integrin alphaMbeta2 binding motif.J Clin Invest. 2007 Nov;117(11):3224-35. doi: 10.1172/JCI30134. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17932565 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinolysis is down-regulated in mouse collagen-induced arthritis, but its normalization does not alleviate the course of disease.Inflamm Res. 2011 Nov;60(11):1021-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0363-0. Epub 2011 Jul 24. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21786185
-
Absence of functional compensation between coagulation factor VIII and plasminogen in double-knockout mice.Blood Adv. 2018 Nov 27;2(22):3126-3136. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018024851. Blood Adv. 2018. PMID: 30459211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saksela O, Rifkin DB: Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1988, 4:93-126 - PubMed
-
- Moscatelli D, Rifkin DB: Membrane and matrix localization of proteinases: a common theme in tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1988, 948:67-85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

