Ion channel gating: a first-passage time analysis of the Kramers type
- PMID: 11891285
- PMCID: PMC122561
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.052015699
Ion channel gating: a first-passage time analysis of the Kramers type
Abstract
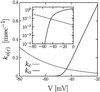
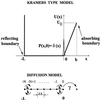
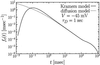
The opening rate of voltage-gated potassium ion channels exhibits a characteristic knee-like turnover where the common exponential voltage dependence changes suddenly into a linear one. An explanation of this puzzling crossover is put forward in terms of a stochastic first passage time analysis. The theory predicts that the exponential voltage dependence correlates with the exponential distribution of closed residence times. This feature occurs at large negative voltages when the channel is predominantly closed. In contrast, the linear part of voltage dependence emerges together with a nonexponential distribution of closed dwelling times with increasing voltage, yielding a large opening rate. Depending on the parameter set, the closed-time distribution displays a power law behavior that extends over several decades.
Figures

References
-
- Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. 3rd Ed. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer; 2001.
-
- Sakmann B, Neher E, editors. Single-Channel Recording. 2nd Ed. New York: Plenum; 1995.
-
- Hänggi P, Talkner P, Borkovec M. Rev Mod Phys. 1990;62:251–342.
-
- Mainen Z F, Joerges J, Huguenard J R, Sejnowski T J. Neuron. 1995;15:1425–1439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

