The tRNA specificity of Thermus thermophilus EF-Tu
- PMID: 11891293
- PMCID: PMC122552
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.052028599
The tRNA specificity of Thermus thermophilus EF-Tu
Abstract
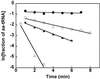
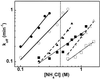
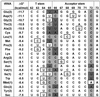
By introducing a GAC anticodon, 21 different Escherichia coli tRNAs were misacylated with either phenylalanine or valine and assayed for their affinity to Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu)*GTP by using a ribonuclease protection assay. The presence of a common esterified amino acid permits the thermodynamic contribution of each tRNA body to the overall affinity to be evaluated. The E. coli elongator tRNAs exhibit a wide range of binding affinities that varied from -11.7 kcal/mol for Val-tRNA(Glu) to -8.1 kcal/mol for Val-tRNA(Tyr), clearly establishing EF-Tu*GTP as a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein. Because the ionic strength dependence of k(off) varied among tRNAs, some of the affinity differences are the results of a different number of phosphate contacts formed between tRNA and protein. Because EF-Tu is known to contact only the phosphodiester backbone of tRNA, the observed specificity must be a consequence of an indirect readout mechanism.
Figures


References
-
- Janiak F, Dell V A, Abrahamson J K, Watson B S, Miller D L, Johnson A E. Biochemistry. 1990;29:4268–4277. - PubMed
-
- Louie A, Ribeiro N S, Reid B R, Jurnak F. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:5010–5016. - PubMed
-
- Louie A, Jurnak F. Biochemistry. 1985;24:6433–6439. - PubMed
-
- Ott G, Schiesswohl M, Kiesewetter S, Forster C, Arnold L, Erdmann V A, Sprinzl M. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1050:222–225. - PubMed
-
- LaRiviere F J, Wolfson A D, Uhlenbeck O C. Science. 2001;294:165–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

