The single-channel properties of human acetylcholine alpha 7 receptors are altered by fusing alpha 7 to the green fluorescent protein
- PMID: 11891309
- PMCID: PMC122630
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.052699599
The single-channel properties of human acetylcholine alpha 7 receptors are altered by fusing alpha 7 to the green fluorescent protein
Abstract
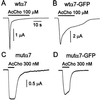
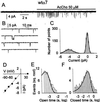
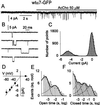
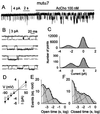
Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine (AcCho) receptors composed of alpha7-subunits (alpha7-AcChoRs) are involved in many physiological activities. Nevertheless, very little is known about their single-channel characteristics. By using outside-out patch-clamp recordings from Xenopus oocytes expressing wild-type (wt) alpha7-AcChoRs, we identified two classes of channel conductance: a low conductance (gamma(L)) of 72 pS and a high one (gamma(H)) of 87 pS, with mean open-times (tau(op)) of 0.6 ms. The same classes of conductances, but longer tau(op) (3 ms), were seen in experiments with chimeric alpha7 receptors in which the wtalpha7 extracellular C terminus was fused to the green fluorescent protein (wtalpha7-GFP AcChoRs). In contrast, channels with three different conductances were gated by AcCho in oocytes expressing alpha7 receptors carrying a Leu-to-Thr 248 mutation (mutalpha7) or oocytes expressing chimeric mutalpha7-GFP receptors. These conductance levels were significantly smaller, and their mean open-times were larger, than those of wtalpha7-AcChoRs. Interestingly, in the absence of AcCho, these oocytes showed single-channel openings of the same conductances, but shorter tau(op), than those activated by AcCho. Accordingly, human homomeric wtalpha7 receptors open channels of high conductance and brief lifetime, and fusion to GFP lengthens their lifetime. In contrast, mutalpha7 receptors open channels of lower conductance and longer lifetime than those gated by wtalpha7-AcChoRs, and these parameters are not greatly altered by fusing the mutalpha7 to GFP. All this evidence shows that GFP-tagging can alter importantly receptor kinetics, a fact that has to be taken into account whenever tagged proteins are used to study their function.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

