Linkage disequilibrium between the beta frequency of the human EEG and a GABAA receptor gene locus
- PMID: 11891318
- PMCID: PMC122592
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.052716399
Linkage disequilibrium between the beta frequency of the human EEG and a GABAA receptor gene locus
Abstract
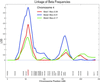
Human brain oscillations represent important features of information processing and are highly heritable. A common feature of beta oscillations (13-28 Hz) is the critical involvement of networks of inhibitory interneurons as pacemakers, gated by gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) action. Advances in molecular and statistical genetics permit examination of quantitative traits such as the beta frequency of the human electroencephalogram in conjunction with DNA markers. We report a significant linkage and linkage disequilibrium between beta frequency and a set of GABA(A) receptor genes. Uncovering the genes influencing brain oscillations provides a better understanding of the neural function involved in information processing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interpopulation linkage disequilibrium patterns of GABRA2 and GABRG1 genes at the GABA cluster locus on human chromosome 4.Genomics. 2008 Jan;91(1):61-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.08.007. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Genomics. 2008. PMID: 17976953 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage and linkage disequilibrium mapping of ERP and EEG phenotypes.Biol Psychol. 2002 Oct;61(1-2):229-48. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0511(02)00060-1. Biol Psychol. 2002. PMID: 12385677
-
Haplotype-based localization of an alcohol dependence gene to the 5q34 {gamma}-aminobutyric acid type A gene cluster.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;62(1):47-55. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.1.47. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15630072
-
[Statistical approaches to gene mapping of human diseases].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2001 Feb;23(1):86-8, 96. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2001. PMID: 12905828 Review. Chinese.
-
Genetics, environment and cognitive abilities: review and work in progress towards a genome scan for quantitative trait locus associations using DNA pooling.Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2001 Apr;40:s41-8. doi: 10.1192/bjp.178.40.s41. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11315224 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial-anatomical mapping of NoGo-P3 in the offspring of alcoholics: evidence of cognitive and neural disinhibition as a risk for alcoholism.Clin Neurophysiol. 2005 May;116(5):1049-61. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2004.12.015. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15826845 Free PMC article.
-
EEG coherence: topography and frequency structure.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Sep;198(1):59-83. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1936-9. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19626316
-
Heritability and molecular-genetic basis of resting EEG activity: a genome-wide association study.Psychophysiology. 2014 Dec;51(12):1225-45. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12344. Psychophysiology. 2014. PMID: 25387704 Free PMC article.
-
Children and adolescents with autism exhibit reduced MEG steady-state gamma responses.Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Aug 1;62(3):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.002. Epub 2006 Sep 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 16950225 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide association analyses of electrophysiological endophenotypes for schizophrenia and psychotic bipolar disorders: a preliminary report.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015 Apr;168B(3):151-61. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32298. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2015. PMID: 25740047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger H. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr. 1929;87:527–570.
-
- Crick F, Koch C. Semin Neurosci. 1990;2:263–275.
-
- Llinas R, Pare D. Neuroscience. 1991;44:521–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

