Reelin function in neural stem cell biology
- PMID: 11891343
- PMCID: PMC122641
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.062698299
Reelin function in neural stem cell biology
Abstract
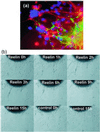
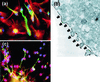
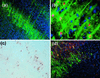
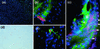
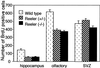
In the adult brain, neural stem cells (NSC) must migrate to express their neuroplastic potential. The addition of recombinant reelin to human NSC (HNSC) cultures facilitates neuronal retraction in the neurospheroid. Because we detected reelin, alpha3-integrin receptor subunits, and disabled-1 immunoreactivity in HNSC cultures, it is possible that integrin-mediated reelin signal transduction is operative in these cultures. To investigate whether reelin is important in the regulation of NSC migration, we injected HNSCs into the lateral ventricle of null reeler and wild-type mice. Four weeks after transplantation, we detected symmetrical migration and extensive neuronal and glial differentiation of transplanted HNSCs in wild-type, but not in reeler mice. In reeler mice, most of the injected HNSCs failed to migrate or to display the typical differentiation pattern. However, a subpopulation of transplanted HNSCs expressing reelin did show a pattern of chain migration in the reeler mouse cortex. We also analyzed the endogenous NSC population in the reeler mouse using bromodeoxyuridine injections. In reeler mice, the endogenous NSC population in the hippocampus and olfactory bulb was significantly reduced compared with wild-type mice; in contrast, endogenous NSCs expressed in the subventricular zonewere preserved. Hence, it seems likely that the lack of endogenous reelin may have disrupted the migration of the NSCs that had proliferated in the SVZ. We suggest that a possible inhibition of NSC migration in psychiatric patients with a reelin deficit may be a potential problem in successful NSC transplantation in these patients.
Figures
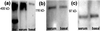

Similar articles
-
Reelin affects chain-migration and differentiation of neural precursor cells.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009 Dec;42(4):341-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.08.006. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19698788
-
Rescue of the reeler phenotype in the dentate gyrus by wild-type coculture is mediated by lipoprotein receptors for Reelin and Disabled 1.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Mar 1;495(1):1-9. doi: 10.1002/cne.20846. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16432903
-
Trajectory Analysis Unveils Reelin's Role in the Directed Migration of Granule Cells in the Dentate Gyrus.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 3;38(1):137-148. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0988-17.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29138282 Free PMC article.
-
[Cytoarchitectonic abnormality in the facial nucleus of the reeler mouse].Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1999 Aug;74(4):411-20. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10496086 Review. Japanese.
-
Integrin and the Reelin-Dab1 pathway: a sticky affair?Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2004 Sep 17;152(2):269-71. doi: 10.1016/j.devbrainres.2004.06.005. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15351515 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of neural stem cell-like cells from bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells.Neurol Res. 2011 Dec;33(10):1083-93. doi: 10.1179/1743132811Y.0000000053. Neurol Res. 2011. PMID: 22196762 Free PMC article.
-
A neurochemical basis for an epigenetic vision of psychiatric disorders (1994-2009).Pharmacol Res. 2011 Oct;64(4):344-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.05.026. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Pharmacol Res. 2011. PMID: 21699980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular form of prion protein inhibits Reelin-mediated shedding of Caspr from the neuronal cell surface to potentiate Caspr-mediated inhibition of neurite outgrowth.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 7;30(27):9292-305. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5657-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20610764 Free PMC article.
-
Control of neuronal migration through rostral migration stream in mice.Anat Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;43(4):269-79. doi: 10.5115/acb.2010.43.4.269. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Anat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21267400 Free PMC article.
-
Altered neuroepithelial morphogenesis and migration defects in iPSC-derived cerebral organoids and 2D neural stem cells in familial bipolar disorder.Oxf Open Neurosci. 2024 Apr 3;3:kvae007. doi: 10.1093/oons/kvae007. eCollection 2024. Oxf Open Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38638145 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

