FOXP2 is not a major susceptibility gene for autism or specific language impairment
- PMID: 11894222
- PMCID: PMC447606
- DOI: 10.1086/339931
FOXP2 is not a major susceptibility gene for autism or specific language impairment
Abstract
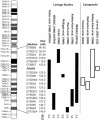
The FOXP2 gene, located on human 7q31 (at the SPCH1 locus), encodes a transcription factor containing a polyglutamine tract and a forkhead domain. FOXP2 is mutated in a severe monogenic form of speech and language impairment, segregating within a single large pedigree, and is also disrupted by a translocation in an isolated case. Several studies of autistic disorder have demonstrated linkage to a similar region of 7q (the AUTS1 locus), leading to the proposal that a single genetic factor on 7q31 contributes to both autism and language disorders. In the present study, we directly evaluate the impact of the FOXP2 gene with regard to both complex language impairments and autism, through use of association and mutation screening analyses. We conclude that coding-region variants in FOXP2 do not underlie the AUTS1 linkage and that the gene is unlikely to play a role in autism or more common forms of language impairment.
Figures
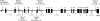
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- ASPEX Linkage Analysis Package, The, ftp://lahmed.stanford.edu/pub/aspex/index.html
-
- BCM Search Launcher, http://searchlauncher.bcm.tmc.edu:9331/seq-util/seq-util.html (for RepeatMasker)
-
- CpG Islands, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/emboss/cpgplot/
-
- dbSNP Home Page, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/
-
- Ensembl Genome Server, http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV). American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
-
- Ashley-Koch A, Wolpert CM, Menold MM, Zaeem L, Basu S, Donnelly SL, Ravan SA, Powell CM, Qumsiyeh MB, Aylsworth AS, Vance JM, Gilbert JR, Wright HH, Abramson RK, DeLong GR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA (1999) Genetic studies of autistic disorder and chromosome 7. Genomics 61:227–236 - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25:63–77 - PubMed
-
- Bishop DV (1994) Is specific language impairment a valid diagnostic criteria? Genetic and psycholinguistic evidence. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 346:105–111 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

