Peripheral blood mononuclear cell activation induced by Leptospira interrogans glycolipoprotein
- PMID: 11895929
- PMCID: PMC127819
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1677-1683.2002
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell activation induced by Leptospira interrogans glycolipoprotein
Abstract
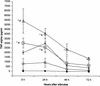
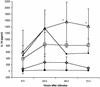
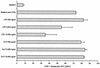
Leptospira interrogans glycolipoprotein (GLP) has been implicated in pathological and functional derangement seen in leptospirosis. The goal of this study was to evaluate GLP's ability to induce cellular activation, as assessed by cytokine production and expression of surface activation markers. GLP extracted from either pathogenic L. interrogans serovar Copenhageni or nonpathogenic Leptospira biflexa serovar Patoc (GLPp) was used to stimulate peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures from healthy donors. Supernatant cytokine levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Expression of CD69 and HLA-DR on lymphocytes and monocytes, as well as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding, were measured by flow cytometry. At 6 h of incubation, GLP induced a significant rise in tumor necrosis factor alpha levels, which dropped progressively until 72 h of incubation. Interleukin-10 peak levels were obtained at between 24 and 48 h, with sustained levels until 72 h of incubation. The response magnitude was proportional to the GLP dose. CD69 expression on T lymphocytes and monocytes increased significantly, as did HLA-DR expression on monocytes. GLPp induced no CD69 or HLA-DR expression. GLP did not block biotinylated LPS binding to monocytes, suggesting that different pathways are used to induce cell activation. In conclusion, GLP induces cellular activation and may play a major role in the pathogenesis of leptospirosis.
Figures
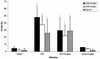

References
-
- Abdulkader, R. C. R., A. C. Seguro, P. S. Malheiro, E. A. Burdmann, and M. Marcondes. 1996. Peculiar electrolytic and hormonal abnormalities in acute renal failure due to leptospirosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 54:1-6. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis, A. O., R. B. Yang, M. R. Mark, S. Suggett, B. Devaux, J. D. Radolf, G. R. Klimpel, P. Godowski, and A. Zychlinsky. 1999. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science 285:736-739. - PubMed
-
- Alves, V. A. F., L. C. C. Gayotto, P. H. Yasuda, A. Wakamatsu, C. T. Kanamura, and T. Brito. 1991. Leptospiral antigens (L. interrogans serogroup ictero-haemorrhagiae) in the kidney of experimentally infected guinea pigs and their relation to the pathogenesis of the renal injury. Exp. Pathol. 42:81-93. - PubMed
-
- Brito, T., G. M. Bohm, and P. H. Yasuda. 1979. Vascular damage in acute experimental leptospirosis of the guinea-pig. J. Pathol. 128:177-181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

