Beta-chemokines are induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and inhibit its growth
- PMID: 11895930
- PMCID: PMC127823
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1684-1693.2002
Beta-chemokines are induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and inhibit its growth
Abstract
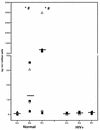
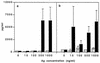
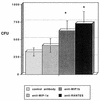
Chemokines (CK) are potent leukocyte activators and chemoattractants and aid in granuloma formation, functions critical for the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. We hypothesized that infection of alveolar macrophages (AM) with different strains of M. tuberculosis elicits distinct profiles of CK, which could be altered by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. RANTES, macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1 alpha), and MIP-1 beta were the major beta-CK produced in response to M. tuberculosis infection. Virulent M. tuberculosis (H37Rv) induced significantly less MIP-1 alpha than did the avirulent strain (H37Ra), while MIP-1 beta and RANTES production was comparable for both strains. MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta were induced by the membrane, but not cytosolic, fraction of M. tuberculosis. M. tuberculosis-induced CK secretion was partly dependent on tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha). AM from HIV-infected individuals produced less TNF-alpha and MIP-1 beta than did normal AM in response to either M. tuberculosis strain. We tested the functional significance of decreased beta-CK secretion by examining the ability of beta-CK to suppress intracellular growth of M. tuberculosis. MIP-1 beta and RANTES suppressed intracellular growth of M. tuberculosis two- to threefold, a novel finding. Thus, beta-CK contribute to the innate immune response to M. tuberculosis infection, and their diminution may promote the intracellular survival of M. tuberculosis.
Figures
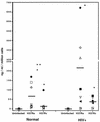
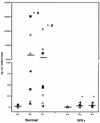
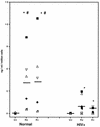
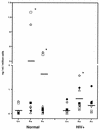
Similar articles
-
Chemokine receptor 5 and its ligands in the immune response to murine tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2005 May;85(3):185-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2004.10.003. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2005. PMID: 15850756
-
Infection of human monocytes with Mycobacterium bovis BCG induces production of CC-chemokines.J Infect. 2003 Aug;47(2):139-47. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(03)00010-0. J Infect. 2003. PMID: 12860148
-
Chemokines induced by infection of mononuclear phagocytes with mycobacteria and present in lung alveoli during active pulmonary tuberculosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998 Sep;19(3):513-21. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.19.3.2815. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9730880
-
beta-Chemokines enhance parasite uptake and promote nitric oxide-dependent microbiostatic activity in murine inflammatory macrophages infected with Trypanosoma cruzi.Infect Immun. 1999 Sep;67(9):4819-26. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4819-4826.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10456936 Free PMC article.
-
MIP-1alpha[CCL3] acting on the CCR1 receptor mediates neutrophil migration in immune inflammation via sequential release of TNF-alpha and LTB4.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Jul;78(1):167-77. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0404237. Epub 2005 Apr 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15831559
Cited by
-
Global gene expression and systems biology analysis of bovine monocyte-derived macrophages in response to in vitro challenge with Mycobacterium bovis.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032034. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384131 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment Particularities in Osteoarticuar Tuberculosis.Curr Health Sci J. 2017 Apr-Jun;43(2):153-158. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.43.02.08. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Curr Health Sci J. 2017. PMID: 30595871 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of gene expression patterns in whole blood discriminate between tuberculosis infection states.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 May 13;14:257. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-257. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24885723 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in Immune Genes and Their Association with Tuberculosis Susceptibility: An Analysis of the African Population.Appl Clin Genet. 2024 Mar 29;17:33-46. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S457395. eCollection 2024. Appl Clin Genet. 2024. PMID: 38567200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor is mediated by PI3-K/MEK1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway.BMB Rep. 2013 Apr;46(4):213-8. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.4.200. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 23615263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agostini, C., M. Facco, M. Siviero, D. Carollo, S. Galvan, A. M. Cattelan, R. Zambello, L. Trentin, and G. Semenzato. 2000. CXC chemokines IP-10 and mig expression and direct migration of pulmonary CD8+/CXCR3+ T cells in the lungs of patients with HIV infection and T-cell alveolitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 162:1466-1473. - PubMed
-
- Appelberg, R. 1994. Protective role of interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-6 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. avium infections. Immunobiology 191:520-525. - PubMed
-
- BAL Cooperative Group Steering Committee. 1990. Bronchoalveolar lavage constituents in healthy individuals, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and selected comparison groups. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 141:S169-S175. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, P., D. Chatterjee, J. Abrams, S. Lu, E. Wang, M. Yamamura, P. Brennan, and R. Modlin. 1992. Cytokine production induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan: relationship to chemical structure. J. Immunol. 149:541-547. - PubMed
-
- Bosco, M., G. Gusella, I. Espinoza-Delgado, D. Longo, and L. Varesio. 1994. Interferon-γ upregulates interleukin-8 gene expression in human monocytic cells by a posttranscriptional mechanism. Blood 83:537-542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

