Type III group B streptococcal polysaccharide induces antibodies that cross-react with Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14
- PMID: 11895934
- PMCID: PMC127872
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1724-1738.2002
Type III group B streptococcal polysaccharide induces antibodies that cross-react with Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14
Abstract
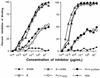
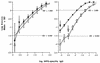
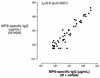
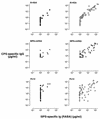
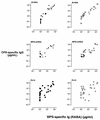
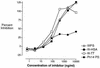
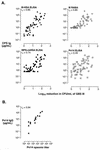
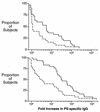
Covalent linkage of a bacterial polysaccharide to a protein greatly enhances the carbohydrate's immunogenicity and its binding to solid surfaces in immunoassays. These findings have spurred the development of glycoconjugate vaccines to prevent serious bacterial infections as well as the use of glycoconjugates as coating antigens in bioassays. We evaluated sera from women immunized with unconjugated group B streptococcal (GBS) type III (GBS III) polysaccharide (IIIPS) or with IIIPS covalently linked to tetanus toxoid to assess specificity, sensitivity, and parallelism in dilution curves in two GBS III enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). One assay used IIIPS mixed with methylated human serum albumin (IIIPS + mHSA) as the coating antigen, and the other used IIIPS covalently linked to HSA (III-HSA). Each coating antigen was associated with a highly specific GBS III bioassay. The sensitivity was higher in the III-HSA ELISA, in which conjugated IIIPS is bound to the plates. Parallelism in titration curves was observed in the III-HSA but not in the IIIPS + mHSA ELISA. The excellent correlation between the concentrations of GBS IIIPS-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and the opsonophagocytic activity of these antibodies indicated that the III-HSA assay can predict functionality of vaccine-induced IgG against GBS III disease. The structure of the repeating unit of the capsular polysaccharide of GBS III differs from that of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 14 (Pn14 PS) only by the presence on GBS III of a sialic acid residue at the end of the side chain. The majority of healthy adults responding to GBS III vaccines with a fourfold or greater increase in GBS III-specific IgG antibodies developed antibodies cross-reacting with Pn14 PS (i.e., desialylated GBS IIIPS). The proportion of GBS vaccine responders who developed IgG to the desialylated IIIPS did not depend on whether IIIPS was given in the unconjugated or conjugated form. When present, these vaccine-induced cross-reacting antibodies conferred in vitro antibody-mediated opsonophagocytosis and killing of both GBS III and Pn14, two pathogens that cause invasive disease in young infants.
Figures
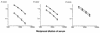
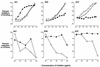
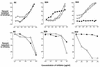
Similar articles
-
Estimation of group B streptococcus type III polysaccharide-specific antibody concentrations in human sera is antigen dependent.Infect Immun. 1998 Dec;66(12):5848-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5848-5853.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9826364 Free PMC article.
-
Structurally identical capsular polysaccharide expressed by intact group B streptococcus versus Streptococcus pneumoniae elicits distinct murine polysaccharide-specific IgG responses in vivo.J Immunol. 2012 Jun 1;188(11):5238-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200132. Epub 2012 Apr 20. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22523389 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response to type III group B streptococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine.J Clin Invest. 1996 Nov 15;98(10):2308-14. doi: 10.1172/JCI119042. J Clin Invest. 1996. PMID: 8941648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Designer vaccines to prevent infections due to group B Streptococcus.Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1995 Oct;107(3):369-73. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1995. PMID: 8608425 Review.
-
Glycoconjugate vaccines to prevent group B streptococcal infections.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003 Sep;3(6):975-84. doi: 10.1517/14712598.3.6.975. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12943456 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformation and Cross-Protection in Group B Streptococcus Serotype III and Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotype 14: A Molecular Modeling Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Feb 13;12(1):28. doi: 10.3390/ph12010028. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30781826 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Kinetics and Response to Routine Vaccinations in Infants Born to Women Who Received an Investigational Trivalent Group B Streptococcus Polysaccharide CRM197-Conjugate Vaccine During Pregnancy.Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 13;65(11):1897-1904. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix666. Clin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29029127 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Understanding the bacterial polysaccharide antigenicity of Streptococcus agalactiae versus Streptococcus pneumoniae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 23;103(21):8149-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602815103. Epub 2006 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16705032 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cell-derived exosomes express a Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide type 14 cross-reactive antigen that induces protective immunoglobulin responses against pneumococcal infection in mice.Infect Immun. 2007 Jan;75(1):220-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01217-06. Epub 2006 Oct 16. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17043104 Free PMC article.
-
Group B streptococcal conjugate vaccines elicit functional antibodies independent of strain O-acetylation.Vaccine. 2009 Jul 16;27(33):4452-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.05.039. Epub 2009 May 31. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 19490960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker, C. J. 1997. Group B streptococcal infections. Clin. Perinatol. 24:59-70. - PubMed
-
- Baker, C. J., and M. S. Edwards. 2001. Group B streptococcal infections, p. 1091-1156. In J. S. Remington and J. O. Klein (ed.), Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant, 5th ed. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Baker, C. J., M. S. Edwards, and D. L. Kasper. 1981. Role of antibody to native type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus in infant infection. Pediatrics 68:544-549. - PubMed
-
- Baker, C. J., and D. L. Kasper. 1976. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 294:753-756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

