Immune responses to recombinant pneumococcal PspA antigen delivered by live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium vaccine
- PMID: 11895935
- PMCID: PMC127874
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1739-1749.2002
Immune responses to recombinant pneumococcal PspA antigen delivered by live attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium vaccine
Abstract
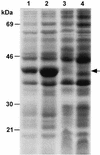
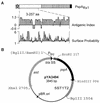
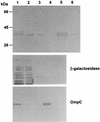
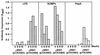
Attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium expressing recombinant antigens from other pathogens elicits primarily a Th1-type dominant immune response to both recombinant and Salmonella antigens. The immunogenicity and appropriate subcellular location of the recombinant antigen in the Salmonella vaccine strain may contribute to augmenting immune responses by facilitating adequate exposure of recombinant antigen to antigen-presenting cells for processing. To allow for secretion from gram-negative bacteria and overexpression of antigen, a DNA fragment encoding a highly antigenic alpha-helical region of PspA (pneumococcal surface protein A) was subcloned downstream from the beta-lactamase signal sequence in the multicopy Asd(+) pYA3493 vector to create pYA3494. pYA3493 was derived from a class of Asd(+) vectors with reduced expression of Asd to minimize selective disadvantage and enhance immunization of expressed recombinant antigens. The S. enterica serovar Typhimurium vaccine strain was constructed by the introduction of deletion mutations Delta crp-28 and Delta asdA16. Approximately 50% of the recombinant PspA (rPspA) expressed in a Salmonella strain harboring pYA3494 was detected in the combined supernatant and periplasmic fractions of broth-grown recombinant Salmonella. After a single oral immunization in BALB/c mice with 10(9) CFU of the recombinant Salmonella vaccine strain carrying pYA3494, immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody responses were stimulated to both the heterologous antigen rPspA and Salmonella lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and outer membrane proteins (OMPs). About half, and even more at later times after immunization, of the antibodies induced to rPspA were IgG1 (indicating a Th2-type response), whereas 60 to 70% of the antibodies to LPS and 80 to 90% of those to OMPs were IgG2a (indicating a Th1-type response). A sublethal infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae WU2 boosted PspA antibody levels and maintained IgG2a/IgG1 ratios similar to those seen before the challenge. Oral immunization with Salmonella-PspA vaccine protected 60% of immunized mice from death after intraperitoneal challenge with 50 times the 50% lethal dose of virulent S. pneumoniae WU2.
Figures

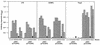
Similar articles
-
PspA family fusion proteins delivered by attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium extend and enhance protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae.Infect Immun. 2009 Oct;77(10):4518-28. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00486-09. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19687204 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses dependent on antigen location in recombinant attenuated Salmonella typhimurium vaccines following oral immunization.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Jul 15;37(2-3):99-104. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00063-4. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12832112
-
A live recombinant avirulent oral Salmonella vaccine expressing pneumococcal surface protein A induces protective responses against Streptococcus pneumoniae.Infect Immun. 1998 Aug;66(8):3744-51. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.8.3744-3751.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9673257 Free PMC article.
-
Live oral Salmonella vaccines: potential use of attenuated strains as carriers of heterologous antigens to the immune system.Parasite Immunol. 1987 Mar;9(2):151-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00496.x. Parasite Immunol. 1987. PMID: 3106921 Review.
-
New technologies in developing recombinant attenuated Salmonella vaccine vectors.Microb Pathog. 2013 May;58:17-28. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Microb Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23142647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A vaccine candidate for post-weaning diarrhea in swine constructed with a live attenuated Salmonella delivering Escherichia coli K88ab, K88ac, FedA, and FedF fimbrial antigens and its immune responses in a murine model.Can J Vet Res. 2012 Jul;76(3):186-94. Can J Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 23277697 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of Salmonella Typhimurium vaccines derived from UK-1 and 14028S: Importance of inherent virulence.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 7;13(9):e0203526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203526. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30192849 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella vaccine vectors displaying delayed antigen synthesis in vivo to enhance immunogenicity.Infect Immun. 2010 Sep;78(9):3969-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00444-10. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20605977 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuning synthesis of Yersinia pestis LcrV from runaway-like replication balanced-lethal plasmid in a Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium vaccine induces protection against a lethal Y. pestis challenge in mice.Infect Immun. 2010 Jun;78(6):2529-43. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00005-10. Epub 2010 Mar 22. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20308296 Free PMC article.
-
The aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase of Edwardsiella ictaluri and its use as balanced-lethal system in fish vaccinology.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 29;5(12):e15944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015944. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21209920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolivar, F., R. L. Rodriguez, P. J. Greene, M. C. Betlach, H. L. Heyneker, and H. W. Boyer. 1977. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 2:95-113. - PubMed
-
- Breiman, R., J. C. Butler, F. C. Tenover, J. Elliot, and R. R. Facklam. 1994. Emergence of drug-resistant pneumococcal infections in the United States. JAMA 271:1831-1835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

