Toxoplasma gondii-infected human myeloid dendritic cells induce T-lymphocyte dysfunction and contact-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 11895936
- PMCID: PMC127822
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1750-1760.2002
Toxoplasma gondii-infected human myeloid dendritic cells induce T-lymphocyte dysfunction and contact-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
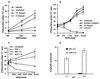
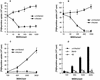
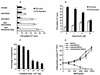
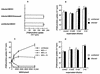
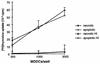
Dendritic cells ignite adaptive immunity by priming naïve T lymphocytes. Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDCs) infected with Toxoplasma gondii induce T-lymphocyte gamma interferon production and may thus activate T. gondii-specific immunity. However, we now demonstrate that T. gondii-infected MDDCs are poor at activating T lymphocytes and are unable to induce specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. On the other hand, MDDCs acquiring nonviable T. gondii antigens directly, or indirectly through captured apoptotic or necrotic cell bodies, induce potent T-lymphocyte activation. T lymphocytes exposed to infected MDDCs are significantly impaired in upregulation of CD69 and CD28, are refractory to activation, and die through contact-dependent apoptosis mediated by an as-yet-unidentified mechanism not requiring Fas, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, leukocyte function antigen 1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 10, alpha interferon, gamma interferon, prostaglandins, or reactive nitrogen intermediates. Bystander T lymphocytes that were neither infected nor apoptotic were refractory to activation, suggesting global dysfunction. Immunosuppression and T-lymphocyte unresponsiveness and apoptosis are typical of acute T. gondii infection. Our data suggest that infected dendritic cells contribute to these processes. On the other hand, host cells infected with T. gondii are resistant to multiple inducers of apoptosis. Thus, regulation of host cell and bystander cell apoptosis by viable T. gondii may be significant components of a strategy to evade immunity and enhance intracellular parasite survival.
Figures

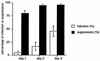

Similar articles
-
Human dendritic cells discriminate between viable and killed Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites: dendritic cell activation after infection with viable parasites results in CD28 and CD40 ligand signaling that controls IL-12-dependent and -independent T cell production of IFN-gamma.J Immunol. 2000 Aug 1;165(3):1498-505. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1498. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10903756
-
A role for inducible costimulator protein in the CD28- independent mechanism of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 15;169(2):937-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.937. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12097399
-
Macrophage-derived dendritic cells have strong Th1-polarizing potential mediated by beta-chemokines rather than IL-12.J Immunol. 2000 Oct 15;165(8):4388-96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.8.4388. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11035076
-
Cell-mediated immunity to Toxoplasma gondii: initiation, regulation and effector function.Immunobiology. 1999 Dec;201(2):240-7. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(99)80064-3. Immunobiology. 1999. PMID: 10631573 Review.
-
From cells to signaling cascades: manipulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Dec 5;39(3):193-203. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00279-7. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14642303 Review.
Cited by
-
Drugs designed to inhibit human p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation treat Toxoplasma gondii and Encephalitozoon cuniculi infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Dec;51(12):4324-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00680-07. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17923491 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of CD4 T-Cells in the spleen of mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii KI-1 tachyzoites.Korean J Parasitol. 2010 Dec;48(4):325-9. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2010.48.4.325. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Korean J Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 21234236 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence of Toxoplasma gondii is associated with distinct dendritic cell responses and reduced numbers of activated CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 2010 Aug 1;185(3):1502-12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903450. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20592284 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus Map protein is an immunomodulator that interferes with T cell-mediated responses.J Clin Invest. 2002 Nov;110(10):1461-71. doi: 10.1172/JCI16318. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12438444 Free PMC article.
-
Primary dendritic cells phagocytose Cryptococcus neoformans via mannose receptors and Fcgamma receptor II for presentation to T lymphocytes.Infect Immun. 2002 Nov;70(11):5972-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.5972-5981.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12379672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Berens, R. L., E. C. Krug, P. B. Nash, and T. J. Curiel. 1998. Selection and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii mutants resistant to artemisinin. J. Infect. Dis. 177:1128-1131. - PubMed
-
- Brinkman, K., S. Debast, R. Sauerwein, F. Ooyman, J. Hiel, and J. Raemaekers. 1998. Toxoplasma retinitis/encephalitis 9 months after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 21:635-636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

